Define Atmospheric Energy - thermodynamics?
The mass of the Earth's atmosphere, p(z), varies with height z above the Earth's surface. Assume that the "thickness" of the atmosphere is adequately small so that it is in a uniform gravitational field of strength g.
a) Write an equation to conclude the atmospheric pressure given the function p(z).
b) In a static atmosphere, each parcel of air has an internal energy ΔEi and a gravitational potential energy ΔEg. To a very good approximation, the air in the atmosphere is an ideal gas with constant specific heat. By means of this assumption, the result of part (a), and classical thermodynamics, shows that the total energy in a vertical column of atmosphere of cross-sectional area A is given by
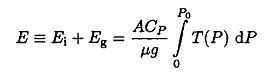
And that the ratio of energies is
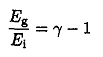
Where T is the temperature, Po is the pressure at the Earth's surface, μ is the molar mass, Cp is the molar specific heat at constant pressure, and g≡Cp/Cv is the ratio of specific heats.
Hint: The above results do not depend on the specific way in which P(z), T(z), and p(z) vary as a function of z (e.g., isothermal, adiabatic, or something intermediate). They depend only on the fact that P(z) is monotonically decreasing. At a few step of the derivation you might find it useful to do integration by parts.