Q. Define Allotropic forms?
All the elements of the group show allotropy. Oxygen exists in two allotropic forms. Dioxygen. 02, is a diatomic gas, paramagnetic in nature. Lewis structure of oxygen molecule with a pair of covalent bonds between two oxygen atoms, as shown in the margin is inadequate in explaining its paramagnetic nature. this structure with all paired electrons is expected to be diamagnetic rather than paramagnetic. Paramagnetism of oxygen can be explained on the basis of Molecular Orbital Theory. The molecular orbital configuration of 0, molecule can be represented as
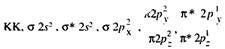
The presence of two unpaired electrons in the antibonding orbitals explains the experimentally observed paramagnetic behaviour.
Ozone, the other allotropic form of oxygen is a triatomic. Pale blue gas. The only method used to make ozone commercially is to pass gaseous oxygen or air though a high voltage electric discharge called a silent electric discharge.
Perhaps you know that the earth is covered by a layer of ozone which protects us from injurious ultraviolet rays coming from the sun. In the upper atmosphere at altitudes ranging from about 15-24 km. ozone is formed in appreciable amounts from oxygen by absorption of ultraviolet radiation from the sun. This radiation first splits O2 molecule into oxygen atoms, which react with O2 molecules to give 03.
hv
O2 --------->2O
O2+o----------------->O3
Ozone also absorbs ultraviolet light. This causes the 0, to decompose and form 0, again.
2O3---------------->3O2
The absorption of uv radiation by O3 serves a twofold purpose. It protects the inhabitants of our planet from injurious radiation and maintains an equilibrium between the concentrations of 0, and 0,. Recently there has been a serious concern about the depletion of this layer. Nitric oxide from emissions of supersonic jets and chlorofluorocarbons used as aerosol propellants and as refrigerants have been identified as the main culprits. There is considerable international effort to save the protective ozone layer.
Sulphur displays allotropy to a remarkable degree. Existing both in a variety of different molecular and physical forms. The molecular species. viz.. S2. S4 S6, and S, are in equilibrium in gaseous sulphur their proportions varying with the temperature. The commonest and the most stable allotrope of sulphur at room temperature is known as'. Rhombic sulphur or a-sulphur. α In rhombic sulphur. S8, rings are arranged in a way Fig. 9.2. That gives a rhombic crystal structure. At 369 K. rhombic sulphur gets converted into monoclinic sulphur or β-sulphur. SF In monoclinic sulphur sx rings are arranged in a monoclinic structure. It is table between 369 and 392 K. At 392 K it melts to produce a liquid containing Sa molecules. S,. At about 433 K the Sa rings open up and join together into long spiral-chain molecules resulting in a thick viscous liquid, p-sulphur, S,. Liquid sulphur boils at 718 K to give gaseous sulphur containing S8 molecules, which dissociate to S6, S4, S2 and finally to sulphur atoms at 2273 K. If liquid sulphur at 463 K is poured into cold water, plastic sulphur or y-sulphur is formed. The allotropy of sulphur as a function of temperature is summarised as follows:
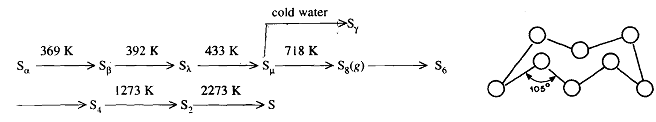
Selenium, tellurium and polonium also exhibit allotropy. Amorphous as well as crystalline forms of selenium and tellurium are known.