Decision Trees - Artificial intelligence:
Suppose you just ever do four things at the weekend: go shopping, watch a film, play tennis or just stay inside. What you do depends on three things: the weather (windy, sunny or rainy); how much money you have (poor or rich) and whether your parents are tripping. You say to your yourself: if my parents are visit, tripping we'll go to the movie. If they're not tripping and also it's sunny, then I'll go for tennis, but if it's windy , and I'm wealthy, then I'll go shopping. If they're not tripping, it's windy and I'm poor, then I will go to the movie. If they're not tripping and it's rainy, then I'll stay inside.
To keep in mind all this, you draw a flowchart which will permit you to read off your conclusion. We call such diagrams decision trees. A fit decision tree for the weekend decision choices would be as follows:
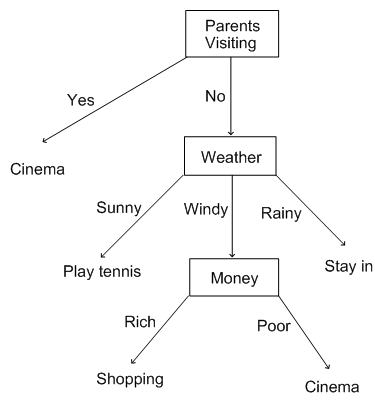
We may see that why such diagrams are called trees, because, while they are admittedly upside down, they start from a root and having branches leading to leaves (the tips of the graph at the downside). Note that the leaves are always decisions, and a particular decision should be at the end of various branches (for example, we might choose to go to the cinema for two different reasons).
Armed with our decision tree, on Saturday morning, when we rise up, all we have to do is check (a) the weather (b) how much money we have and (c) whether our parent's car is parked in the drive. The decision tree will then allow us to form our choice. assume, for example, that the parents haven't turned up and the sun is shining. Then this way through our decision tree will tell us what to do:
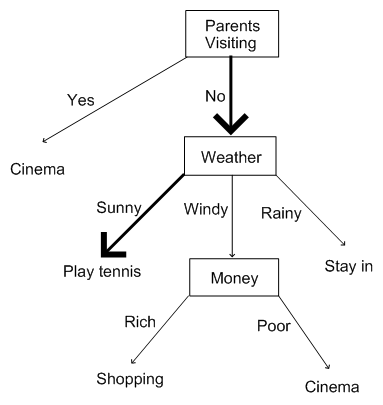
and hence we run off to play tennis because our decision tree informed us to. Notice that the decision tree covers all eventualities. That is, there are no values that the weather conditions, the parents turning up or the money condition must take which aren't provided for in the decision tree. Note that, in this lecture, we will be looking at how to repeatedly produce choice trees from examples, not at how to turn thought methods into decision trees.