Dataflow Computing
A different to the von Neumann model of computation is the dataflow computation model. In a dataflow model, control is fixed to the flow of data. The order of commands in the program plays no role on the implementation order. Execution of an instruction can take place when all the information needed by the instruction is available. Data is in continuous flow
Independent of reusable memory cells and its ease of use initiate execution. Since, data is available for several instructions at the same time; these instructions can be executed in parallel.
For the purpose of exploiting parallelism in totalling Data Flow Graph notation is used to signify computations. In a data flow graph, the nodes shows instructions of the program and the edges shows data dependency between instructions. We can take as an ex, the dataflow graph for the order
z = w × (x+y) is shown in Figure 2.
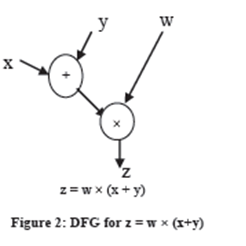
Data moves on the boundaries of the graph in the variety of data tokens, which includes data values and status information. This asynchronous parallel computation is resolute by the firing rule, which is expressed by way of tokens: a node of DFG can shoot if there is a token on each of its input edges. If a node fires, it takes the input tokens, present the associated operation and places result tokens on the output edge. Graph nodes can be only instructions or tasks comprising multiple instructions.
The benefit of the dataflow concept is that nodes of DFG can be self-scheduled. But, the hardware support to recognize the ease of use of necessary data is much more difficult than the von Neumann model. The pattern of dataflow computer includes MIT Tagged Token Data Flow architecture and Manchester Data Flow Machine.