Data hazards - computer architecture:
A main effect of pipelining is to alter the relative timing of instructions by overlapping their execution. This introduces control hazards and data. Data hazards take place when the pipeline changes the order of read/write accesses to operands so that the order differs from the order seen by in sequence executing instructions on the un pipelined machine.
Assume the pipelined execution of these instructions:
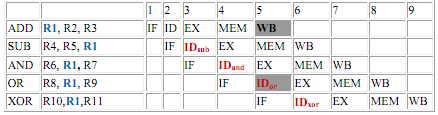
All of the instructions after the ADD instruction use the result of the ADD instruction (in R1). Instruction ADD writes the value of R1 in the WB stage (indicated black), and the SUB instruction reads the value at the time ID stage (ID sub). This difficulty is called a data hazard. Unless safety measures are taken to prevent it, the SUB instruction will read the incorrect value and try to use it.
The AND instruction is also affected by this data hazard. The write of R1 does not finish till the end of cycle 5 (indicated black). Therefore, the AND instruction that reads the registers during cycle 4 (ID and) will receive the incorrect result.
The OR instruction can be made to operate without incurring a hazard by a easy implementation technique. This technique is used to perform register file reads in the second half of the cycle, and writes in the first half. Because WB for ADD both instruction and ID or for OR are performed in 1 cycle 5, the write to register file by ADD instruction will perform in the first half of the cycle, and the read of registers by OR will perform in the second half of the cycle. The XOR instruction operates correctly, because its register read taken place in cycle 6 after the register write by instruction ADD.
The next page described forwarding, a technique to remove the stalls for the hazard involving the SUB and AND both instructions.
We will also categorize the data hazards and consider the cases when stalls cannot be removed. We will see what compiler can do to schedule the pipeline to ignore stalls.
A hazard is build whenever there is dependence amongst instructions, and they are close sufficient that the overlap caused by pipelining would change the order of access to an operand. Our instance hazards have all been with register operands, but it is also possible to build dependence by reading and writing the similar memory location. In DLX pipeline, though, memory references are always kept in order, prevent this type of hazard from arising.
All the data hazards described here involve registers within the CPU. By convention, the hazards are named by the ordering in the program that has to be preserved by the pipeline.
