Cursors
The Oracle uses work areas to execute the SQL statements and to store process information. A PL/SQL construct known as the cursor. Let's you assume name a work area and access its stored information. There are 2 kinds of cursors: implicit and explicit. The PL/SQL implicitly declares a cursor for all the SQL data manipulation, together with queries that return only one row. For queries which return more than one row, you can explicitly declare the cursor to process the rows separately. An example is as shown:
DECLARE
CURSOR c1 IS
SELECT empno, ename, job FROM emp WHERE deptno = 20;
The set of rows returned by a multi-row query is known as result set. The size is the number of rows that meet your search criteria. As the figure shows, an explicit cursor points to the current row in the result set. This permits your program to process the rows one at a time.
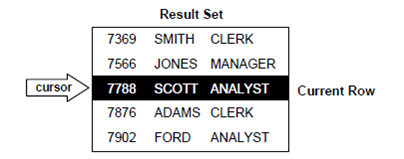
Figure: Query Processing
The Multi-row query processing is somewhat like the file processing. For e.g., a COBOL program opens a file, processes records, and then closes the file. Similarly, a PL/SQL program opens a cursor, then processes rows returned by a query, and then closes the cursor. Now as a file pointer marks the current position in an open file, a cursor notes the current position in a result set.
You use the OPEN, CLOSE, and FETCH statements to control a cursor. The OPEN statement executes the query related with the cursor, identifies the result set, & positions the cursor before the first row. The FETCH statement retrieves the current row and advances the cursor to the next row. If the last row has been processed, the cursor is then disabling by the CLOSE statement.