Cursor Variables:
To execute the multi-row query, the Oracle opens an unnamed work region that stores the processing information. You can use an explicit cursor that names the work region, to access the information. Or, you can use the cursor variable that points to the work region. While a cursor always refers to similar query work region, a cursor variable can refer to various work regions. To create the cursor variables, you can define a REF CURSOR type, and then declare the cursor variables of that type.
The Cursor variables are such as C or Pascal pointers that hold the memory location (address) of a little item rather of the item itself. Therefore, declaring a cursor variable build a pointer, not an item.
Keyword and Parameter Description:
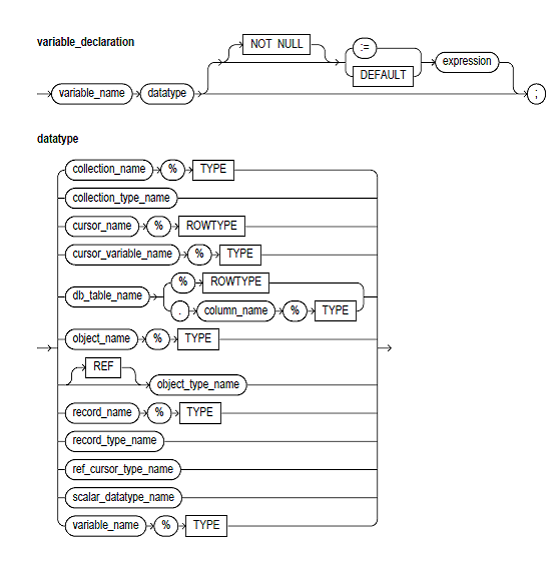
type_name:
This is a user-defined type specifier that is used in the subsequent declarations of the PL/SQL cursor variables.
REF CURSOR:
In PL/SQL, the pointers have datatype REF X, where REF is short form of REFERENCE and
X stands for the class of objects. And hence, the cursor variables have datatype REF CURSOR.
RETURN:
This keyword introduces the RETURN clause that specifies the datatype of the cursor variable result value. You can use the %ROWTYPE attribute in the RETURN clause to give a record type which presents a row in a database table or a row returned by a cursor or strongly typed cursor variable. You can also use the %TYPE attribute to give the datatype of a earlier declared record.
cursor_name:
These identify an explicit cursor earlier declared within the present scope.
cursor_variable_name:
These identify a PL/SQL cursor variable formerly declared within the present scope.
record_name:
These identify a user-defined record formerly declared within the present scope.
record_type_name:
These identify a RECORD type formerly defined within the present scope.
db_table_name:
These identify a database table (or view) that shuld be accessible when the declaration is elaborated.
%ROWTYPE:
These attributes provides a record type that presents a row in the database table or a row fetched from the cursor or strongly typed cursor variable. The Fields in the record and equivalent columns in the row have similar names and datatypes.
%TYPE:
These attributes provides the datatype of a formerly declared user-defined record.