Cursor Variables
Similar to a cursor, cursor variable points to the current row in the result set of a multi-row query. But, dissimilar a cursor, a cursor variable can be opened for any type-compatible query. It is not tied to a specific query. The Cursor variables are true PL/SQL variables, to which you can assign new values and can pass to subprograms stored in an Oracle database. This gives you a convenient way and more flexibility to centralize data retrieval.
Normally, you open a cursor variable by passing it to a stored procedure that declares a cursor variable as one of its formal parameters. The following process opens the cursor variable generic_cv for the chosen query:
PROCEDURE open_cv (generic_cv IN OUT GenericCurTyp,choice NUMBER) IS BEGIN
IF choice = 1 THEN
OPEN generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM emp; ELSIF choice = 2 THEN
OPEN generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM dept; ELSIF choice = 3 THEN
OPEN generic_cv FOR SELECT * FROM salgrade; END IF;
Attributes
The PL/SQL variables and cursors have attributes that are properties that let you reference the datatype and structure of an item without repeating its definition. The Database columns and tables have same attributes that you can use to ease maintenance. A percent sign (%) serves as the attribute indicator.
%TYPE
The %TYPE attribute provides the datatype of a variable or database column. This is principally useful when declaring variables that will hold database values. For example, suppose there is a column named title in a table named books. To declare a variable named my_title which has the same datatype as column title, use dot notation and the %TYPE attribute, as shown:
my_title books.title%TYPE;
Declaring my_title with %TYPE has two benefits. First, you do not require knowing the exact datatype of the title. Second, if you change the database definition of title (make it a big character string for example), the datatype of my_title changes consequently at run time.
%ROWTYPE
The PL/SQL, records are used to group data. A record consists of a number of related fields in which the data values can be stored. The %ROWTYPE attribute gives a record type that shows a row in a table. The record can store a whole row of data selected from the table or fetched from a cursor or cursor variable.
The Columns in a row and corresponding fields in a record have similar names and datatypes. In the illustration below, you declare a record named dept_rec. Its fields have similar names and datatypes as the columns in the dept table.
DECLARE
dept_rec dept%ROWTYPE; -- declare record variable
You use dot notation to reference the fields, as the example below shows:
my_deptno := dept_rec.deptno;
If you declare a cursor which retrieves the job title, last name, salary and hire date of an employee, you can use %ROWTYPE to declare a record that stores similar information, as shown:
DECLARE
CURSOR c1 IS
SELECT ename, sal, hiredate, job FROM emp;
emp_rec c1%ROWTYPE;
-- declare record variable that represents
-- a row fetched from the emp table
When you execute the statement
FETCH c1 INTO emp_rec;
The value in the ename column of the emp table is assigned to the ename field of emp_rec, the value in the sal column is assigned to the sal field, and so on. Figure represents how the result might appear.
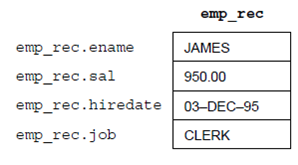
Figure: %ROWTYPE Record emp_rec