Cursor Attributes
The Cursors and cursor variables have 4 attributes which give you helpful information about the execution of a data manipulation statement.
Syntax:
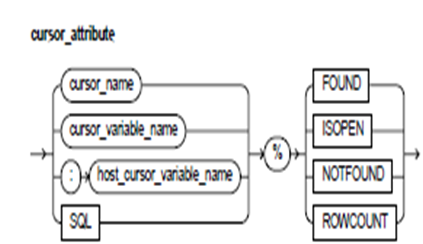
Keyword and Parameter Description:
cursor_name:
These identify an explicit cursor formerly declared within the present scope.
cursor_variable_name:
These identify the PL/SQL cursor variable (or parameter) formerly declared within the present scope.
host_cursor_variable_name:
These identify a cursor variable declared in the PL/SQL host atmosphere and passed to the PL/SQL as a bind variable. The host cursor variable datatype is well-suited with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable. The host variables should be prefixed with a colon.
SQL:
These are the name of the implicit SQL cursor.
%FOUND:
This is a cursor attribute that can be appended to the name of the cursor or cursor variable. Previous to the first fetch from an open cursor, the cursor_name%FOUND results NULL. Afterward, it results TRUE if the final fetch returned a row, or FALSE if the final fetch failed to return a row. Until the SQL statement is executed, the SQL%FOUND results NULL. Afterward, it results TRUE if the statement affects any rows, or FALSE if it affects no rows.
%ISOPEN:
This is a cursor attribute that can be appended to the name of the cursor or cursor variable. If a cursor is open, the cursor_name%ISOPEN results TRUE; Or else, it results FALSE. The Oracle automatically closes the implicit SQL cursor after executing its related SQL statement, Therefore the SQL%ISOPEN always results FALSE.
%NOTFOUND:
This is a cursor attribute that can be appended to the name of the cursor or cursor variable. Previous to the first fetch from an open cursor, the cursor_name%NOTFOUND results NULL. Afterward, it results FALSE if the last fetch returned a row, or TRUE if the last fetch unsuccessful to return a row.
Until a SQL statement is executed, the SQL%NOTFOUND results NULL. Afterward, it results FALSE if the statement affects any rows, or TRUE if it affects no rows.
%ROWCOUNT:
This is a cursor attribute that can be appended to the name of the cursor or cursor variable. If a cursor is opened, the %ROWCOUNT is zeroed. Before the first fetch, the cursor_name%ROWCOUNT yields to 0. Afterward, it results the number of rows fetch so far. The number is incremented if the newest fetch returned a row. Until the SQL statement is executed, the SQL%ROWCOUNT results NULL. Afterward, it results the number of rows affected by the statement. The SQL%ROWCOUNT results 0 if the statement affect no rows.