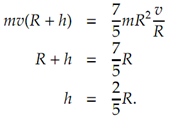Q. Cue Ball Slip Problems?
A cue ball is struck beside a line through its centre and parallel to the table. It moves forward primarily with zero angular rotation, sliding across the felt however eventually rolls without slipping. How far does it travel prior to pure rolling motion occurs?
This interesting problem yields to elementary linear and rotational kinematics. It's worth making some preliminary observations about the problem.
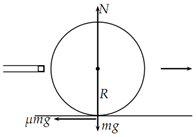
First the preliminary linear velocity imparted to the cue ball v0+ = v is a maximum at the moment of impact During the course of travel the velocity will decrease because of the frictional drag exerted by the table felt on the ball. At the similar time a torque will be exerted on the ball by this same frictional force. Even though the problem doesn't require consideration of kinetic energy it is clear that the initial kinetic energy is purely linear and when slippage stops the resulting kinetic energy is distributed between linear kinetic energy and rotational kinetic energy. The normal force N at any time is simply because of gravity and is mg. The frictional force because of drag is then µmg where µ is the coefficient of friction. The drag is conscientious for the only acceleration on the cue ball.
The velocity at any time is
vt = v + at = v - µgt.
The torque τ is µmgR however τ = Iα where I is the moment of inertia and α is the angular acceleration. As it is known that the moment of inertia of a solid sphere about its centre is
2/5(mr2),
We are able to solve for the angular acceleration.
α =τ/I=(µmgR)/(2/5(mR2))=(5/2)(µg/R)
The angular velocity is ωt = ω0 + αt where ω0 is zero therefore
ωt = αt =(5/2)(µg/R)t.
Pure rolling motion take place when vt = Rωt Substituting and solving for t
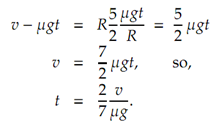
We are able to now find the distance from d = vt + ½ at.
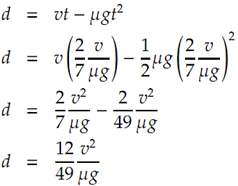
At what point must a cue ball be struck so that it immediately rolls with no slipping?
The objective here is to instruct a rotational velocity as well as a linear velocity such that the equation
v = ωR
is satisfied.
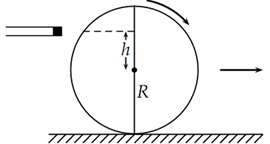
This problem is able to be recast in the following form: At what point should the cue ball be struck so that the ball rotates around its point of contact with the table? The condition is valid at the moment of impact although subsequent movement of the ball will be constrained by the table surface.
We begin by finding the moment of inactivity of the ball around the point of contact. Using the parallel axis theorem, Ip = Ig + mk2, where Ig is the moment of inertia around the centre of mass and k is the distance from the centre of mass to the new point of rotation. This new point is one radius absent from the centre.
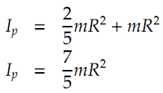
The impulse at themoment of impact results in a change ofmomentumF′ = mv. Note that v0 = 0. The corresponding change in angular momentum is F′ (R + h) = Ip ω. We now have, substituting