The cross-section of exogenous tree is as shown in given figure.The following components are visible to the naked eye:
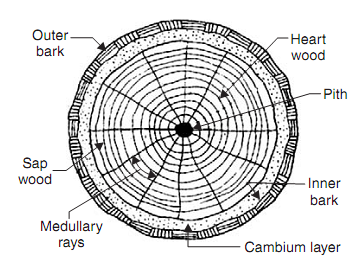
Cross-section of exogeneous tree
1. Pith: It is the inner most part of the tree and therefore the oldest part of exogeneous tree when the plant becomes old, the pith dies and becomes and dark and fibrous. It varies in shape and size
2. Heart Wood: It is the portion surrounding pith. It is strong and dark in color. This portion is useful for several engineering purpose. It is the dead part of wood. It consists of various annular rings.
3. Sap Wood: It is the layer next to heart wood. It denotes contains sap and recent growth. It takes active part in the growth of trees by permitting sap to move in upward direction. Annual rings of sap wood are less sharply divided and are light in color. The sap wood is also called as alburnum.
4. Cambium Layer: It is a thin layer of fresh sap lying among sap wood and the inner bark. It has sap which is not still converted into sap wood. If the bark is removed & cambium layer is exposed to atmosphere then cells cease to be active and tree dies.
5. Inner Bark: It is a inner skin of tree defensive the cambium layer. It provides protection to cambium layer.
6. Outer Bark: It is the outer skin of the tree and contain of wood fibres. Sometimes it contains cracks and fissures.
7. Medullary Rags: These are thin radial fibers extending from pith to cambium layer. They together hold annular rings. In some of trees they are broken and some other they cannot be prominent.