Program: Creation of a Circular linked list
ALGORITHM (Insertion of an element into a Circular Linked List)
Step 1 Begin
Step 2 if the list is empty or new element comes before the start (head) element, then insert the new element as start element.
Step 3 else, if the new element comes after the last element, then insert the new element at the end element and adjust the pointer of last element to the start element.
Step 4 else, insert the new element in the list by using the find function. find function returns to the address of the found element to the insert_list function.
Step 5 End.
If new item is to be added after an existing element, then, call the find function recursively to trace the 'key' element. The new element is added before the 'key' element using above algorithm.
Figure demonstrated the Circular linked list with a new element that is to be inserted. Figure depicts a Circular linked list along with the new element added between first & second nodes of Figure.
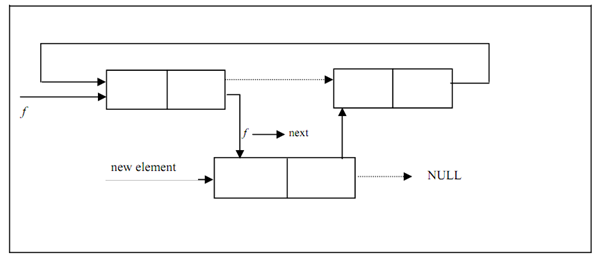
Figure: A Circular Linked List after insertion of the new element between first and second nodes
(Dotted lines depict the links prior to insertion)
Program demonstrated the code for insertion of a node into a Circular linked list.
#include
#include
#define NULL 0 structlinked_list
{
int data;
structlinked_list *next;
};
typedefstructlinked_listclist;
clist *head, *s;
/* prototype of find and insert functions */
clist * find(clist *, int);
clist * insert_clist(clist *);
/*definition of insert_clist function */
clist * insert_clist(clist *start)
{
clist *n, *n1;
int key, x;
printf("Insert new value for the new element");
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("eneter key element");
scanf("%d",&key);
if(start->data ==key)
}
else
{
n=(clist *)malloc(sizeof(clist));
n->data=x;
n->next = start;
start=n;
n1 = find(start, key);
if(n1 == NULL)
printf("\n not found \n");
else
{
n=(clist*)malloc(sizeof(clist));
n->data=x;
n->next=n1->next;
n1->next=n;
}
}return(start);
/*description of find function */
clist * find(clist *start, int key)
{
if(start->next->data == key)
return(start);
if(start->next->next == NULL)
return(NULL);
else
find(start->next, key);
}
void main()
{
voidcreate_clist(clist *);
int count(clist *);
void traverse(clist *);
head=(clist *)malloc(sizeof(clist));
s=head;
create_clist(head);
printf(" \n traversing the created clist and the starting address is %u \n",traverse(head);
printf("\n number of elements in the clist %d \n", count(head));
head=insert_clist(head);
printf("\n traversing the clist after insert_clist& starting address is %u \n",head);
traverse(head);
}
voidcreate_clist(clist *start)
{
printf("input element -1111 for coming out of loop\n");
scanf("%d", &start->data);
if(start->data == -1111)
start->next=s;
else
{
start->next=(clist*)malloc(sizeof(clist));
create_clist(start->next);
} }
void traverse(clist *start)
{
if(start->next!=s)
{
printf("data is %d \t next element address is %u\n", start->data, start- traverse(start->next);
}
}
if(start->next == s)
printf("data is %d \t next element address is %u\n",start->data, start->next);
int count(clist *start)
{
if(start->next == s)
return 0;
else
return(1+count(start->next));
}