Cause and Effect
Even a highly significant correlation does not necessarily mean that a cause and effect relationship exists between the two variables. Thus, correlation does not necessarily imply causation or functional relationship though the existence of causation always implies correlation or association between variables. It might sometimes happen that a fair degree of correlation is observed between the two variables but this is only due to chance as the theory might indicate non-existence of cause and effect relationship. Such a correlation is known as spurious correlation. While interpreting the correlation coefficient, it is necessary to see whether there is any cause and effect relationship between the variables under study. If there is no such relationship, the correlation observed is meaningless.
Figure 1
Ferrochrome is a material used in the manufacture of stainless steel. Suppose, in recent times there has been such a large increase in the supply of ferrochrome worldwide that its international price has dropped.
The simplified figure above reveals that as supply increased from S1 to S2, prices fell from P1 to P2. Hence, there is an inverse correlation between supply and price, that is, when supply increases, prices fall. Further we can say that the increase in supply was the CAUSE that led to the EFFECT of falling prices. So far so good.
Now consider the figure given below:
Figure 2
Here we have plotted supply against price. We may now be tempted to say that the fall in price from P1 to P2 was the CAUSE that led to the EFFECT of increase in supply from S1 to S2. This does not make economic sense because a fall in price does not lead to an increase in supply. The problem is that we have reversed the cause (increase in supply) and the effect (fall in price).
Continuing the example, suppose supply increases from S1 to S2, but demand increases by a disproportionately larger quantity. As demand increases more than supply the price will increase. In such a case if we plot price against supply the simplified graph would be as follows:
Figure 3
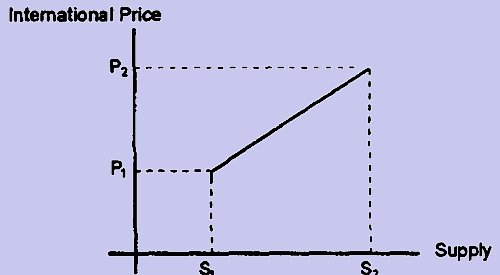
Hence, when supply increases from S1 to S2, price increases from P1 to P2. This is again poor economics because an increase in supply should reduce prices and not increase prices. The problem here is that the main CAUSE for the increase in price is the disproportionate increase in demand which is not shown in the graph. Hence, by ignoring the vital factor of demand and by comparing supply with price we come up with a spurious positive correlation between supply and price which defies good economics.