Expertsmind.com brings you unique solution in electrical engineering
- A constellation is a region of the sky with well defined borders; familiar star patterns help us locate these constellations.
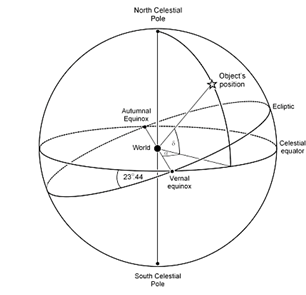
- To help us understand and map the sky. For reference, we identify 4 special points:-
- The north celestial pole is the point directly over the Earth's North Pole
- The south celestial pole '' '' '' '' " South Pole
- The celestial equator , which is a projection of Earth's equator into space,
makes a complete circle around the celestial sphere.
- The ecliptic is the path the sun follows as it appears to circle around the
celestial sphere once each year. (23.5 degrees; same as earth)
Local sky
-The point directly overhead (90 degrees perpendicular) is the Zenith.
- The meridian is an imaginary line stretching between the 2 opposite sides of the horizon.
- We can pinpoint the position of any object in the local sky by stating its direction/azimuth and its altitude above the horizon.
- Angular size of an object is the angle it appears to span in your field of view. The farther away an object is the smaller its angular size.
- Angular distance between a pair of objects in the sky is the angle that appears to separate them in your field of view.
- Latitude measure the north-south position on earth. (0 degrees at equator , 90 at north pole & affects constellations)
Longitude measures east-west position. (is defined to be 0 degress along a line passing through Greenwich, England.
-
- The Seasons change every 3 months starting in summer; June
- Lunar phases are the cycle of which the moon changes appearance and the time at which it rises.
- Lunar eclipse occurs when Earth lies directly between the Sun and the Moon, so that the Earth's shadow falls on the moon
- There are 3 types of lunar eclipses:-
- 1- Total lunar eclipse
2-partial lunar eclipse
- 3- penumbral eclipse
- Solar eclipse occurs when the moon lies in between the sun and the earth and so sun will completely or partially blocked.
1 Arseconnd:- The width of a finger at arm's length is about 1 degree. Remember that there are 60 arcminutes in 1 degree and 60 arcseconds in 1 arcminute.
Anglular size = Physical size
360 ° 2 ¶ x distance
Ex. The angular diameter on the moon is about 0.5 degrees and the moon is about 380,000 km away. What is the Moon's physical diameter?
Solution
0.5 x 380,000
360° 2 ¶ x distance
=3316
= 3300 (rounded to nearest hundred) ¯
- The sun is highest up the sky during its equinoxes; spring and fall.