Constants and Variables:
You can declare the constants and variables in the declarative section of any PL/SQL subprogram, block, or package. The Declarations allot the storage space for a value that specify its datatype, and name the storage space location so that you can reference it. The Declarations can also assign an initial value and enforce the NOT NULL constraint.
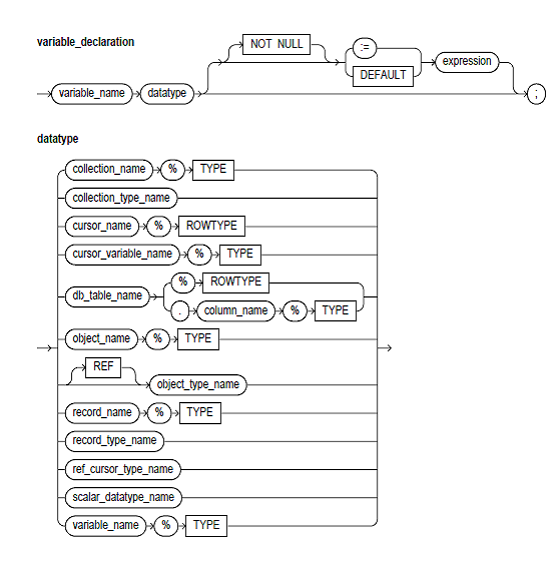
Keyword and Parameter Description:
constant_name:
These identify the program constant.
CONSTANT:
These keywords indicate the declaration of a constant. You should initialize a constant in its declaration. The value of a constant cannot be changed if once it is initialized.
record_name.field_name:
These identify the field in a user-defined or %ROWTYPE record formerly declared within the present scope.
scalar_type_name:
These identify a predefined scalar datatype like the BOOLEAN, NUMBER, or VARCHAR2.
db_table_name.column_name:
These identify a database table and column that should be available when the declaration is elaborated.
variable_name:
These identify the program variable.
collection_name:
These identify the nested table, index-by table, or varray earlier declared within the present scope.
cursor_name:
These identify an explicit cursor formerly declared within the present scope.
cursor_variable_name:
These identify a PL/SQL cursor variable formerly declared within the present scope.
object_name:
These identify an object (or instance of the object type) formerly declared within the present scope.
record_name:
These identify a user-defined record formerly declared within the present scope.
db_table_name:
These identify a database table (or view) that should be available when the declaration is elaborated.
%ROWTYPE:
This attribute gives a record type that presents a row in the database table or a row fetched from a formerly declared cursor. The Fields in the record and corresponding columns in the row have similar names and datatypes.
%TYPE:
This attribute gives the datatype of a formerly declared collection, field, cursor variable, object, record, database column, or variable.
NOT NULL:
These constraints prevent the assigning of the nulls to a variable or constant. At run time, trying to assign the null to a variable defined as NOT NULL raises the predefined exception VALUE_ERROR. The constraint NOT NULL should be followed by an initialization clause.
Expression:
This is a randomly complex combination of the variables, literals, constants, operators, and function calls. The easiest expression consists of a single variable. If the declaration is elaborated, the value of the expression is assigned to the constant or variable. The value and the constant or variable should have compatible datatypes.