Connection Establishment
TCP transmits data in full duplex mode. When two TCP is two machines are connected they are able to send segments to each other simultaneously. This implies that each party must initialize communication and get approval from the other party before any data are transferred.
Three way handshaking. The connection establishment in TCP is called three way handshaking. In our example an application program called the client wants to make a connection with other application program called the server using TCP as the transport layer protocols.
The process starts with server. The programs tells its TCP that it is ready to accept a connection. This is called a request for a passive open. Although the server TCP ready to accept any connection from any machine in the world it can make the connection itself.
The client program issues a request for an active open. If client that wishes to connect to an open server tells its TCP that it needs to be connected to that particular server TCP can now start the way handshaking process as shown in figure few fields necessary to understand each phase the sequence number the acknowledgment number the control flags and the window size if not empty. The three step in this phase are as follows:
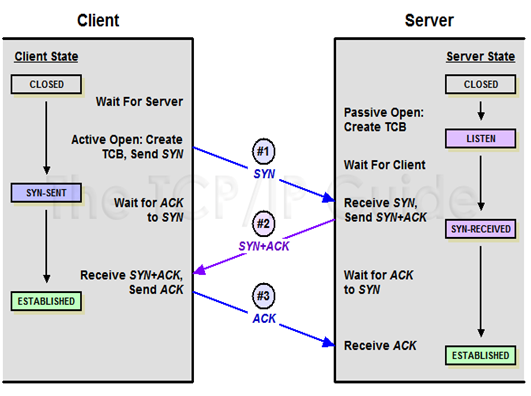
Figure Connection establishment using three way handshaking
a.The client sends the first segment a SYN segment in which only the SYN flag is set. This segment is for synchronization of sequence number. It consumes one sequence number when the data transfer starts. The sequence number is incremented by. We can say that the SYN segment carries no real data but we can think of it as containing imaginary byte.
b.The server sends the second segment a SYN + ACK segment with 2 flag SYN and ACK. This segment has a dual purpose. It is a SYN segment for communication in the other direction and server as the acknowledgment in the other direction and server the acknowledgment for the SYN segment. It consumes one sequence number.
c.The client sends the third segment. This is just an ACK segment it acknowledges the receipt of the second segment with the ACK flag and acknowledges the receipt of the second segment with the ACK flag and acknowledgment number field. Note that the sequence number in this segment is the same as the one in the SYN segment the ACK segment does not consume any sequence number.
The connection establishment procedure in TCP is susceptible to a serious security problem called the SYN flooding Attack. This happens when malicious attacker send a large number of SYN segments to a server pretending that each of them is coming from a different client by faking the source IP address in the datagram's. The server assuming that the clients are issuing an active open all orates the necessary resources such as creating communication tables and setting timers. The TCP server then sends the SYN+ ACK segments to the fake client which are lost. During this time however a lot of resource are occupied without being used. If during this short time the number of SYN segments is the server eventually runs out of resources and may crash. This SYN flooding attack belongs to a type of security attack known as a denial of service attack in which an attacker monopolizes a system with so many service requests that the system collapses and denies service to every request.