Conditionals - SQL
At first sight SQL does not appear to have a single operator for expressing logical implication. In this respect it would be in common with most programming languages, including Tutorial D. However, standard SQL defines a partial ordering for its three truth values, under which false is deemed to precede true. Thus, the comparisons p < q, p > q, p <= q, and p >= q are all supported in standard SQL (in addition to p = q, of course).
it is noted that in 2VL p → q is equivalent to ¬ p ∨ q. Study of Figure 3.5 reveals that ¬ p ∨ q does indeed equate to p → q when neither operand is unknown, and the same is true of p <= q! (It is the pronunciation, "is less than or equal to", rather than "implies", that led to my observation that SQL appears to include direct support for a 3VL form of implication by accident.)
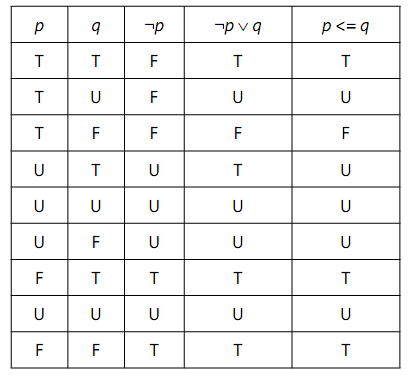
Figure: The SQL Truth Tables for ¬ p∨ q and p <= q
Note, however, that p <= q is not equivalent to ¬ p ∨ q. Intuitively, we understand that "p implies q" is true whenever q is true. This holds for ¬ p ∨ q but not for p <= q, as the row for p = U and q = T shows. The U in the last column for that row arises from SQL's general rule that whenever an operand of a comparison is NULL, the result is unknown-and NULL, when it is the result of evaluating a Boolean expression, is considered synonymous with unknown. In fact, Figure gives a demonstration of the fact that SQL is not always faithful to its own concept, that NULL represents "a value exists here but we don't know which value". What U really means when it appears in the column for p <= q is that <= is undefined for that particular pair of truth values.