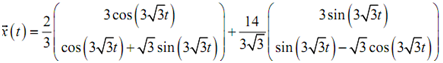Complex numbers from the eigenvector and the eigenvalue.
Example1: Solve the following IVP.
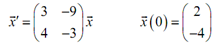
We first require the eigenvalues and eigenvectors for the given matrix.
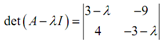
= l2 + 27
l1,2 = + 3 √(3i)
Therefore, now that we have the eigenvalues recall which we only need to determine the eigenvector for one of the eigenvalues as we can determine the second eigenvector for free from the first eigenvector as:
l1 = 3 √(3i),
We have to to solve the subsequent system.
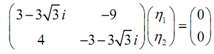
By using the first equation we find,
(3 - 3 √(3i)) h1- 9h2 = 0,
h2 = 1/3 (1 - (√(3i))) h1
Therefore, the first eigenvector is,
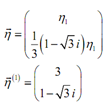
h1 = 3
While finding the eigenvectors during these cases ensures that the complex number appears in the numerator of any fractions as we'll require this in the numerator later on. Also attempt to clear out any fractions by suitably picking the constant. It will make our life simple down the road.
Here, the second eigenvector is,
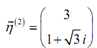
Though, as we will see we won't require this eigenvector.
The solution which we get from the first eigenvalue and eigenvector is,
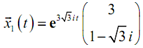
Therefore, as we can notice there are complex numbers in both the exponential and vector that we will require to get rid of in order to use that as a solution. Recall from the complex roots section of the second order differential equation section which we can use Euler's formula to find the complex number out of the exponential. Doing it, we get
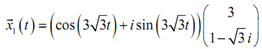
The subsequent step is to multiply the cosines and sines in the vector.
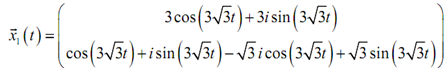
Here combine the terms along with an "i" in them and split such terms off from those terms that don't include an "i". Also factor the "i" out of that vector.
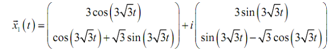
= u?(t) +v?(t)
Here, it can be demonstrated as u?(t) and v?(t)are two linearly independent solutions to the system of differential equations. It means that we can utilize them to form a general solution and both they are real solutions.
Therefore, the general solution to a system along with complex roots is,
x? (t) = c1u?(t) +c2v?(t)
Here u?(t) and v?(t)are found by writing the first solution as:
x? (t) = u?(t) + i v?(t)
For our system so, the general solution is,
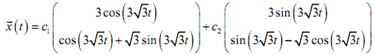
We now require applying the initial condition to it to find the constants,
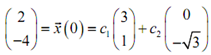
This leads to the subsequent system of equations to be solved,
3c1 = 2;
c1 + √3c2 = -4;
By solving both equations we get:
c1 = (2/3) and c2 = (14/3√3)
The actual solution is, so,