Collection Methods:
The collection method is a built-in function or procedure which operates on the collections and is called using the dot notation. The methods like the COUNT, EXISTS, LIMIT, FIRST, LAST, NEXT, EXTEND, PRIOR, TRIM, & DELETE helpful to normalize the code, make collections easier to use, and make your applications easier to sustain.
The COUNT, EXISTS, LIMIT, PRIOR, FIRST, LAST, and NEXT are the functions, that appear as part of an expression. The TRIM, EXTEND, and DELETE are the procedures, that appear as a statement. The EXISTS, NEXT, PRIOR, TRIM, EXTEND, and DELETE take integer parameters.
Syntax:
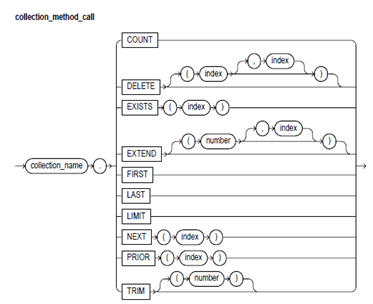
Keyword and Parameter Description
collection_name:
These identify an index-by table, varray, or nested table formerly declared within the present scope.
COUNT:
The COUNT returns to the number of elements which a collection presently contains, that is helpful as the present size of a collection is not always known. You can use the COUNT wherever an integer expression is allowed.
For varrays, the COUNT always equals to LAST. For nested tables, generally, COUNT equals to LAST. But, if you delete elements from the middle of the nested table, the COUNT is smaller than LAST.
DELETE:
This procedure has 3 forms. The DELETE eliminates all the elements from a collection. The DELETE (n) eliminates the nth element from a nested table. If n is null, the DELETE (n) does nothing. The DELETE (m,n) eliminates all the elements in the range of m..n from a nested table. If m is bigger than n or if m or n is null, then DELETE (m,n) does nothing.
Index:
This is an expression which should yield an integer.
EXISTS:
The EXISTS(n) returns TRUE when the nth element in a collection exists. Or else, EXISTS(n) returns FALSE. Primarily, you can use EXISTS with DELETE to sustain the sparse nested tables. You can also use the EXISTS to avoid raising an exception whenever you reference a nonexistent element. When passed an out-of-range subscript, the EXISTS returns FALSE rather than of raising the SUBSCRIPT_OUTSIDE_LIMIT.
EXTEND:
This procedure has 3 forms. The EXTEND appends one null element to the collection. The EXTEND(n) appends n null elements to the collection. The EXTEND(n,i) appends n copies of the ith element to the collection. The EXTEND operates on the internal size of the collection. Therefore, if EXTEND encounters deleted elements, it involves them in its tally.
FIRST, LAST:
The FIRST & LAST return the first & last (lowest limit & upper limit) index numbers in a collection. If the collection is blank, the FIRST and LAST return NULL. When the collections contain only one element, the FIRST and LAST return similar index number. For varrays, the FIRST always returns 1 and the LAST always equals to COUNT. For the nested tables, generally, LAST equals to COUNT. But, when you delete elements from the middle of the nested table, the LAST is larger than COUNT.
LIMIT:
For the nested tables, which have no maximum size, the LIMIT returns NULL. For varrays, the LIMIT returns the maximum number of elements which a varray can contain (that you should specify in its type definition).
NEXT, PRIOR:
The PRIOR(n) returns the index number which precedes an index n in a collection. The NEXT(n) returns the index number which succeed index n. If n has no predecessor, then the PRIOR(n) returns NULL. Similarly, if n has no successor, the NEXT(n) returns the NULL.
TRIM:
This procedure has 2 forms. The TRIM eliminates one element from the end of the collection. The TRIM(n) eliuminates n elements from the end of the collection. If n is bigger than COUNT, then the TRIM(n) raises the SUBSCRIPT_BEYOND_COUNT. The TRIM operates on the internal size of a collection. Therefore, if TRIM encounters deleted elements, it involves them in its tally.