What is CMMI?
This is a collection of instructions an organization can follow with the purpose to gain the better control over its software development process.
According to the SEI, there are 5 levels of the CMMI.
Level 1 - Initial
At maturity level 1, the processes are usually ad hoc and the organization usually does not give a stable environment. The Success in these organizations depends on the competence and heroics of people in the organization and not on the use of the proven processes. Instead of this chaotic environment, ad hoc, maturity level 1 organizations often produce products and services that work; however, they frequently exceed the budget and schedule of their projects.
The Maturity level 1 organizations are characterized by a tendency to over commit, abandon processes in the time of crisis, and not be able to repeat their past successes again.
Level 2 - Repeatable
At the maturity level 2, the software development successes are repeatable. The organization may use some basic project management to track the cost and schedule.
The Process discipline helps to ensure that the existing practices are retained during the times of stress. When these practices are in place, projects are performed & managed according to their documented plans.
Project status and the delivery of services are visible to the management at defined points (for e.g., at leading milestones and at the completion of major tasks).
The Basic project management processes are established to track the functionality, schedule, & cost. The necessary process discipline is in place to repeat earlier successes on projects with same applications.
Level 3 - Defined
At maturity level 3, the processes are well characterized and understood, and are described in the procedures, standards, tools, and methods.
The organization's set of standard processes, which is the basis for level 3, is established & improved over time. These standard methods are used to establish consistency across the organization. The Projects establish their defined processes by the organizations set of standard processes according to the tailoring guidelines
The organization's management establishes process objectives based on the organization's set of standard processes & ensures that these objectives are appropriately addressed.
The critical difference between level 2 & level 3 is the scope of process descriptions, standards, and procedures. At the level 2, the standards, process descriptions, and procedures might be quite different in each specific instance of the process (for e.g., on a particular project). At the level 3, the process descriptions, the standards, and procedures for a project are tailored from the organization's set of standard processes to suit a particular project or organizational unit.
Level 4 - Managed
Using the precise measurements, the management can effectively control the software development effort. In particular, management can identify the ways to adjust and adapt the process to particular projects without measurable losses of quality or deviations from specifications.
The Sub processes are selected that significantly contribute to overall process performance. These selected sub processes are controlled by using statistical and other quantitative methods.
A critical difference between the maturity level 3 and maturity level 4 is the predictability of the process performance. At the maturity level 4, the performance of processes is controlled by using statistical and other quantitative methods, and is quantitatively predictable. At the maturity level 3, processes are only qualitatively predictable.
Level 5 - Optimizing
The Maturity level 5 focuses on persistently improving the process performance through both incremental and innovative technological improvements. The Quantitative process improvement objectives for the organization are established, continually revised to reflect modifying business objectives, and used as criteria in managing process improvement. The effects of deployed process improvements are measured and evaluated against the quantitative process-improvement objectives. Both the defined processes and the organization set of standard processes are targets of measurable improvement activities.
Process improvements to address common causes of process variation and measurably improve the organization's processes are evaluated, identified, and deployed.
The Optimizing processes that are adaptable, nimble and innovative depend on the participation of an empowered workforce aligned with the business values and objectives of the organization. The organization's ability to rapidly respond to changes and opportunities is enhanced by finding the way to accelerate and share learning.
A critical difference between maturity level 4 and maturity level 5 is the type of process variation addressed. At the maturity level 4, processes are concerned with addressing special causes of process variation and providing the statistical predictability of the results. Though processes may produce predictable results, the results may be insufficient to achieve the established objectives. At the maturity level 5, the processes are concerned with addressing common causes of process variation and changing the process (i.e., shifting the mean of the process performance) to improve process performance (while maintaining the statistical probability) to achieve the established quantitative process-improvement objectives.
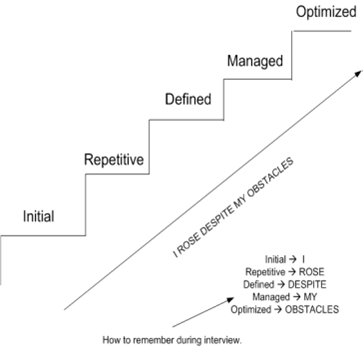
Figure: - CMMI Levels