Classifying critical points : Let's classify critical points as relative maximums, relative minimums or neither minimums or maximums.
Fermat's Theorem told us that all relative extrema (provided the derivative presents at that point of course) of a function will be critical points. The given graph has two relative extrema and both takes place at critical points as the Fermat's Theorem predicted. Note that we've got a critical point which isn't a relative extrema ( x =0 ). it is okay since Fermat's theorem doesn't say that all critical points will be relative extrema. Only it states that relative extrema will be critical points.
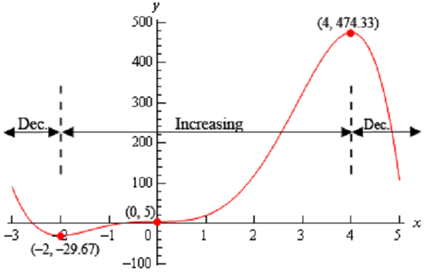
In the sketch of the graph we can illustrated that to the left of x = -2 the graph is decreasing & to the right of x = -2 the graph is increasing & x = -2 is a relative minimum. In other terms, the graph is behaving around the minimum accurately as it ought to be in order for x = -2 to be a minimum. The similar thing can be said for the relative maximum at x = 4 . The graph is raising on the left and falling on the right exactly as it have to be in order for x = 4 to be a maximum. At last, the graph is increasing on both of sides of x = 0 & therefore this critical point can't be a minimum or a maximum.
These ideas can be generalized to arrive at a way to test if a critical point is a relative maximum, relative minimum, or neither. If x = c is a critical point and the function is decreasing to the left of x = c & it is rising to the right then x = c have to be a relative minimum of the function. Similarly, if the function is rising to the left of x = c and decreasing to the right then x = c have to be a relative maximum of the function. At last, if the function is rising on both sides of x = c or decreasing on both of the sides of x = c then x = c can be neither a relative minimum nor a relative maximum.
These ideas can be summarized up in the given test.
First Derivative Test
Suppose that x = c is a critical point of f ( x ) then,
1. If f ′ ( x ) = 0 to the left of x = c and f ′ ( x ) = 0 to the right of x = c then x = c is a relative maximum.
2. If f ′ ( x ) = 0 to the left of x = c & f ′ ( x ) = 0 to the right of x = c then x = c is a relative minimum.
3. If f ′ ( x ) is the similar sign on both sides of x = c then x = c is neither a relative maximum nor a relative minimum.
It is significant to note here that the first derivative test will just classify critical points as relative extrema and not as absolute extrema. Absolute extrema are largest & smallest function values and might not even exist or be critical points if they do present.
The first derivative test is accurately that, a test by the first derivative. It doesn't ever utilizes the value of the function and thus no conclusions can be plotted from the test regarding the relative "size" of the function at the critical points (that would be required to identify absolute extrema) and can't even start to address the fact that absolute extrema might not takes place at critical points.