Classification of Information Systems
Information systems may be classified in different ways for different purposes. One method of classification is by the application area. Another method of classification is by the type of service rendered, where the following categories are typical:
1) Computing Service Systems that provide a general Computing service to a number of users;
2) Information Storage and Retrieval Systems;
3) Command and Control Systems built to monitor some given situation and provide a signal when predefined conditions occur;
4) Transaction Processing Systems designed to process predefined transactions and produce predefined outputs as well as maintain the necessary database;
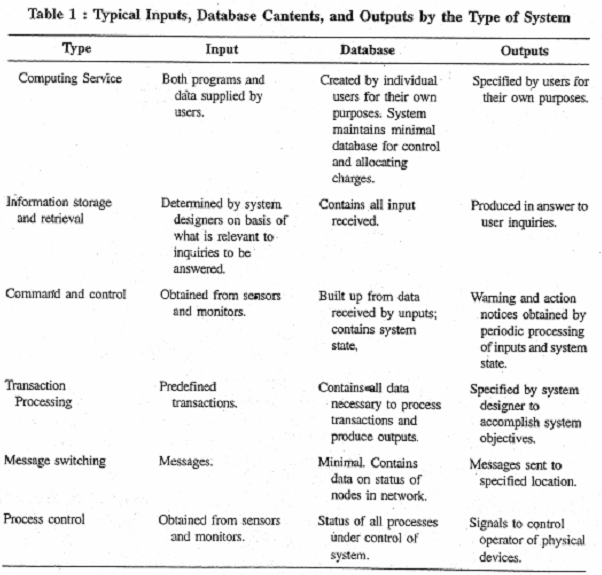
5) Message Switching Systems;
6) Process Control Systems which are designed to control physical processes by monitoring the conditions and signalling appropriate action.
Information Systems may be classified by the type and degree of interaction with the user arid/ or the environment. Some examples are: Batch Processing Systems, Interactive Systems, Real Time, or Online Systems, etc.
Each of these types of systems has certain characteristics that affect its structure, the measures of performance that are appropriate, and the process of designing, building and operating the system.
The different ways of classification described above are useful in identifying common features of systems that may appear in more than one type. It may also be mentioned here that the uses of systems and the technology on which systems are developed are continuously changing, as are the organisations using them. Therefore, systems are never static.