CLASSICAL VIEW ON UNEMPLOYMENT
The classical economists as we observed in Unit 1 of this course, were of the view that full employment prevailed in the economy all the time. This was consistent with the view that whatever amount of labour was supplied got demanded by firms. A basic assumption in the classical framework was the flexibility in wage rate and prices. Thus the gap between supply of and demand for labour got wiped out through adjustments in wage rate.
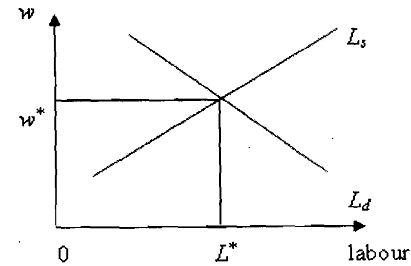
Fig. : Equilibrium Level of Employment
In Fig. we measure real wage rate (w) on y-axis and quantity of labour (L) on x-axis. The equilibrium wage rate reached through interaction of supply of labour (L,) and demand for labour (Ld) is W* and quantity of labour employed is L*, which represents full employment.
The aggregate supply curve according to classical economists is a vertical straight line at the full employment output level. At the equilibrium wage rate everyone seeking employment gets engaged. If the wage rate is above w (see Fig.) there is excess supply of labour compared to its demand. In their efforts to get employed some of the currently unemployed workers will be willing to work at a wage lower than the prevailing one and in the process will bring down the wage rate till it reaches w*. On the other hand, when wage rate is below w* there will be excess demand compared to supply. Due to shortage of labour firms will compete with each other and will be willing to pay higher wage, as a result of which wage rate will increase. Remember that classical economists were concerned with real wage in the economy, which is W defined as the ratio of nominal wage (W) to price level (P) such that w = -. P Thus flexibility in real wage assured that a rise in price level is accompanied by a proportionate rise in nominal wage. In fact the dichotomy between real and monetary sectors of the economy, as envisaged in classical model, ensures such proportional changes. The classical economists did not rule out the possibility of decrease in nominal wage rate. Nonetheless, it was always in response to decrease in money supply and price level. In theory, the classical model appears to have a sound base. When compared with reality, however, it does not explain the obvious phenomenon of unemployment in the economy. As we will see below, there is much rigidity in the economy, which does not allow smooth and instantaneous changes in wage rate. Moreover, some amount of frictional unemployment is always present in an economy as workers switch over from one job to another. The neoclassical economists recognized the limitations of classical model and made amendments to the classical position of zero unemployment. They assumed that the economy in normal times has certain minimum unemployment called 'natural rate of unemployment'.