Both L1 and L2 are SL2. (You should verify this by thinking about what the automata look like.)
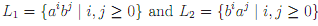
We claim that L1 ∪ L2 ∈ SL2. To see this, suppose, by way of contradiction, that it was SL2. Then it would satisfy Suffx Substitution Closure. But abb ∈ L1 ∪ L2, since it is in L1, and bba ∈ L1 ∪ L2, since it is in L2, and, by Suffx Substitution Closure, this implies that aba ∈ L1 ∪ L2, which is not the case. Hence, L1 ∪ L2 is not SL2.
It's important to not misunderstand the weight of this result. It does not show that every union of two SL2 languages is not SL2-after all, the union of any SL2 language with itself must, necessarily, be SL2. It is easy to come up with pairs of distinct SL2 languages which yield an SL2 union as well,
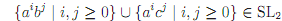
What it does say is that one can't count on the union of SL2 languages being SL2. This is in contrast to the closure result for intersection, which lets us build up languages out of simpler SL2 languages using intersection with con?dence that the result will be SL2. Showing that our desired language is the union of some simple SL2 languages doesn't help us. The result may or may not be SL.