Choosing Output in Long Run
* In long run, a firm can change all its inputs, including size of the plant.
* We are taking free entry and free exit.
* Accounting Profit and Economic Profit
- Accounting profit (π) = R - wL
- Economic profit (π) = R - wL - rK
- wL = labor cost
- rk = opportunity cost of capital
* Long Run Competitive Equilibrium
- Zero-Profit
- If R > wL + rk, the economic profits are positive
- If R = wL + rk, zero economic profits, but firms is earning normal rate of return; showing that the industry is competitive
- If R < wl + rk, consider going out of the business
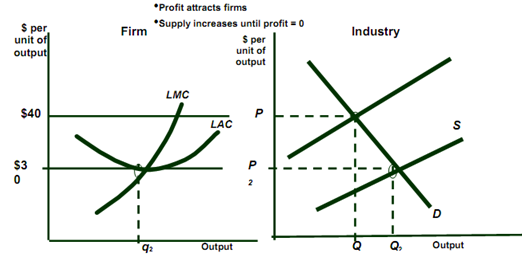
- Entry and Exit
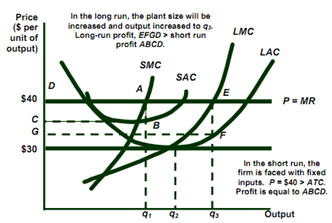
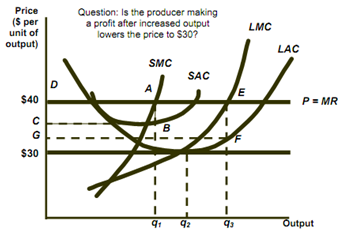
• The long run response to short run profits is to increase profits and output.
- Profits will attract the other producers.
- More producers increase the supply of industry that lowers market price.
Long Run Competitive Equilibrium
* Long Run Competitive Equilibrium
1) MC = MR
2) P = LAC
- No incentive to enter or leave
- Profit = 0
3) Equilibrium Market Price
* Questions
1) Explain market adjustment when P < LAC and firms are having identical costs.
2) Explain market adjustment when firms are having different costs.
3) What is opportunity cost of land?