Changes in Market Equilibrium
Equilibrium prices are known by the associate level of supply and demand.
Supply and demand are decided by particular values of supply & demand determining variables.
Alteration in any one or combination of these variables can result in a change in the equilibrium price and/or quantity.
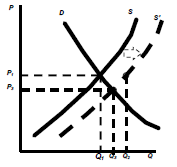
Raw material prices fall
– S moves to S’
– Surplus @ P1 of Q1, Q2
– Equilibrium @ P3, Q3
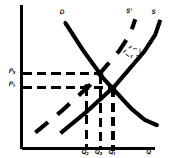
Raw material prices increases
– S moves to S’
– Shortage @ P1 of Q1, Q2
– Equilibrium @ P3, Q3
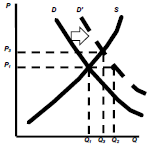
Income Rises
P D D’ S
– Demand moves to D’ Shortage @ P1 of Q1, Q2
– Equilibrium @ P3, Q3
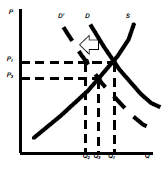
Income Reduces
– Demand moves to D’
– Surplus @ P1 of Q1, Q2
– Equilibrium @ P3, Q3
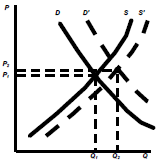
Income Rises & raw material prices fall
– The increase in D is more than the increase in S
– Equilibrium price and quantity rise to P2, Q2
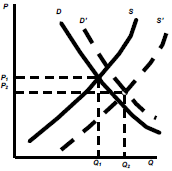
Income Increases & raw material prices decreases
– The rise in D is less than the increase in S
– Equilibrium price reduce to P2and quantity rise to Q2
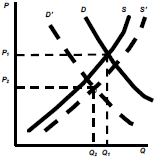
Income Decreases & raw material prices decreases
D’
– The decrease in D is more than the increase in S
– Equilibrium price and quantity lowers to P2 Q2
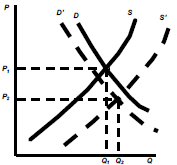
Income decreases & raw material prices decreases
– The decrease in D is less than the rise in S
– Equilibrium price reduce to P2 and quantity increase to Q2