The Cash Cycle: so as to deal with the problem of cash management we should have a concept about the flow of cash by a firm's accounts. The entire process of such cash flow is identified as Cash Cycle. It has been demonstrated in the figures 2 and 3. Cash is used to purchase materials from that goods are produced. Production of such goods includes use of funds for paying wages and meeting the other expenses.
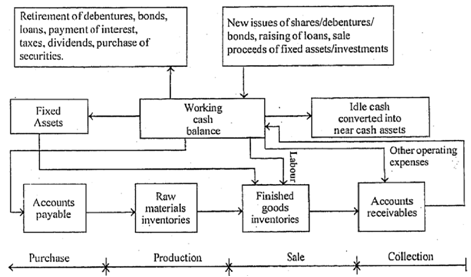
Figure: The cash cycle
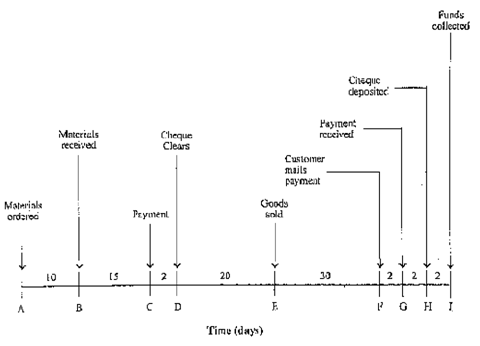
Figure: Details of the Cash Cycle
Goods generated are sold either on cash or credit. In the last case the pending bills are acquired at a later date. The firm hence receives cash instantly or later for the goods sold through it. The cycle keeps repeating itself.
The diagram in the figure 2 only provides a common idea about the channels of flow of cash in a business. In terms of time, the magnitude of the flow is depicted in the diagram specified in the figure 3. The subsequent information is reflected by the figure 3.
- Raw material for production is acquired 10 days after placement of order.
- The material is transformed in goods for sale in 37 days (15+2+20) from point of B to E.
- The payment for material purchased can be deferred to 17 days i.e. 15+2, after this is received that is the distance of time among points B to D, assuming that this takes 2 days for collection of payment of the cheque.
- The amount of the bill for goods sold is acquired 32 days (30+2) after the sale of goods as is depicted with duration of time among point E to G.
- The recovery of cash spent until point D is made after 56 days (20+30+2+2+2) as demonstrated between points D to J.