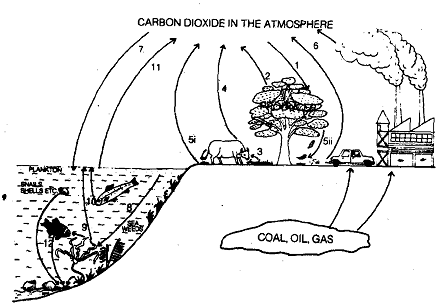
The Carbon Cycle: We have seen that carbon is one of the essential elements of all organic substances and it enters the ecosystem through the process of photosynthesis. Carbon is present as carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide forms 0.03 to 0.04% of the atmosphere. The oceans also have carbon dioxide dissolved in their water. For understanding the cyclic processes related to carbon, you are advised to go through the 12 basic steps of the cycle, as indicated in Fig. Please note numbers 1 to 12 in the figure. Each of these numbers denotes a component process of the cycle. When you see number 1 in the figure, observe what it shows and read its explanation under point 1 of the carbon cycle.
1) You have already studied that carbon dioxide enters food webs through plants by the process of photosynthesis.
2) you have also studied that some of the carbon dioxide captured by the plants and converted into organic molecules, is returned to the atmosphere via respiration.
3) And some portion of the carbon is incorporated into the plant body, which is later passed on to the herbivores, etc.
4) The living beings release carbon dioxide into air during breathing.
5) (i, ii) carbon dioxide is also returned to the atmospheric reservoir by the death and subsequent decay of the dead bodies and wastes of animals and plants.
6) Formation of fossil fuels, like coal. oil. gas, is a part of the carbon cycle. wherein carbon is trapped for millions of years. Fossil fuels are the remains of ancient plants and animals that were subjected to high temperature and pressure over millions of years. Man has been using wood, peat, coal and petroleum as sources of energy, for running transport. such as motorcars. aeroplanec etc.: for industries. for cooking food and var~ous other purposes. While considering fossi :uels as energy packed substances. you must not forget that it is the energy of sunlight from prehistoric times that remains stored in them in chemical form.
7) Since air is in direct contact with the sea, the carbon dioxide from the air dissolves in the upper layers of water resulting in the formation of carbonates.
8) The plants that grow in sea water, do not get atmospheric carbon dioxide. Therefore, they utilise carbonates present in water as a source of carbon dioxide during photosynthesis.
9) Food produced by water plants passes through the aquatic food chain. For example, when fish feed on the water plants, carbon passes on from plants to the fish, and ultimately to the other organisms that feed on fish.
10) Some of the carbon dioxide by marine plants and'animals during breathing gets dissolved in sea water and can be re-utilised by the plants.
11) However. some of the carbon dioxide. thus evolved. escapes to the atmosphere.
12) Organisms like snails, oysters etc.. extract carbon dioxide dissolwd in water and combine it with calcium to form calcium carbonate from which they construct their shells. Shells of these dead animals collect in undersea deposits and may eventually be converted to limestone.