Calculation of Receiving End Voltage
Consider the simple circuit shown in Figure.
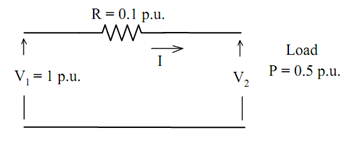
To find the voltage V2 using analytical method:
P = I V2 = 0.5 ..... (1)
V2 = V1 - R I ..... (2)
V2 = 1 - 0.1 I
∴ 0.5 = I ( 1 - 0.1 I ) = I - 0.1 I2
or I2 - 10 I + 5 = 0 ..... (3)
So I = 10 + √ 100 -20 / 2 = 10 + 8.944272 / 2 = 0.527864 or 9.472 p.u.
∴ V2 = 1 - 0.1 × 0.527864 = 0.9472136 p.u.
Using I = 9.472 p.u. gives an unacceptable solution.
Using iterative method, V2 may be found as:
(i) Assume V2 (call it 1V2)
(ii) Find I = P / V2
(iii) Find ?V = R I
(iv) Find new value of V2 = V1 - R I ( call it 2V2)
(v) Check |2 V2 - 1V2|
Solving the previous example by the iterative method gives:
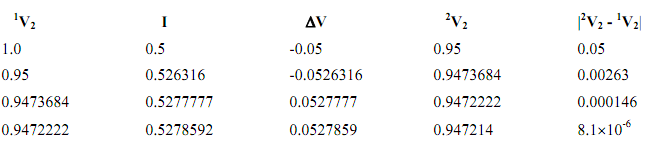
Notice the improvement in the new value of V2 and the absolute error |2V2 - 1V2|. The calculation may be terminated at the end of any iteration depending on the required accuracy |2V2 - 1V2|.