In most real signal processing applications the measured signals can not be described by an analytical expression. In addition, by the Wold decomposition theorem a stationary signal can be represented as a sum of its predictable part and its stochastic part. Here, we focus on stochastic signals. Real signals are generally random (stochastic) in nature and therefore, it is only possible to de?ne their statistical properties. A simple discrete random signal may be generated from within MATLAB with the rand function (generates a zero-mean white Gaussian noise signal).
a) Generate a length 1000 discrete random signal x, a bold font is used to emphasise that it is a random signal, and display the result with the stem function.
Observe that although this signal can clearly not be represented by an analytical expression, there is a degree of uniformity along its length, i.e. thestatistical properties of the signal are not time-varying. Such a signal is said to be statistically stationary.
- Use the MATLAB documentation to discover more about the rand function and how it generates random numbers.
- Calculate the theoretical mean value for this signal; this quantity can be estimated from x with
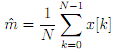
where m' is the so-called sample mean, the circum?ex denotes that the quantity is an estimate.
- Use the mean function within MATLAB to perform this calculation for x. How accurate is this estimate?
- Calculate the standard deviation for this signal; estimate this quantity with the std function which is based upon and
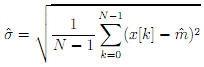
is referred to as the standard deviation.
- Use the rand function to generate, in turn, nine more length 1000 random signals and calculate sample mean and standard deviations
for each signal. Plot the sample mean and standard deviations values for the ten signals and show they cluster about the true values.
What can you say about the bias of these estimators?
The mean and standard deviation are two quantities which describe the statistical properties of a statistically stationary random signal.
To obtain a complete statistical description of the signal it is necessary to examine the probability density function from which each time
sample is drawn.
- Use the hist function to approximate the probability density function for one of the length 1000 x signals (The true probability density function would be obtained if the output from hist was scaled by the number of points in x). Comment upon the result, in particular, what function will it converge to as the length of x becomes very large?