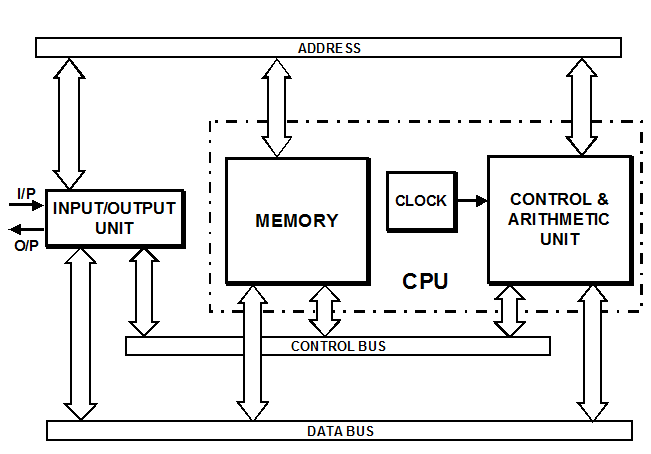
BUSES
It can be seen from Figure 4 that there are three buses - the data bus, the address bus, and the control bus. Each bus consists of a group of parallel wires.
The data bus transfers data between memory, CPU and I/O units, under the control of signals sent through the control bus. For example, if data is to be transferred (sent) from the CPU to a memory location, the control unit within the CPU places an output instruction on the CPU, and write instruction on the memory unit. When the data arrives at the memory, it must be written into the memory at a given address. The address is already present, having been sent by the CPU along the address bus. Hence, data is stored at the memory address given. Note that if the transfer had been from the CPU to an I/O device, the address of the I/O device would have been given.
The address bus is one-way only. The control bus usually has one set of wires for input sensing lines, and one set for output controls.
Data buses are usually bi-directional; that is, data is either transferred, or fetched along the same set of wires. The control unit usually decides in which direction data will travel. If there are several peripherals, and these all wish to use the CPU at the same time, some method of priority must be established. There are various ways of achieving this. One method uses the control unit to select the lucky peripheral, whilst another method lets the peripherals themselves automatically decide which peripheral takes control.