Bulk Binds advantages
In the Embedded Oracle RDBMS, the PL/SQL engines accept any valid PL/SQL subprogram or block. As the figure shows, the PL/SQL engine executes all procedural statements but sends SQL statements to the SQL engine that executes the SQL statements and, in many cases, returns the data to the PL/SQL engine.
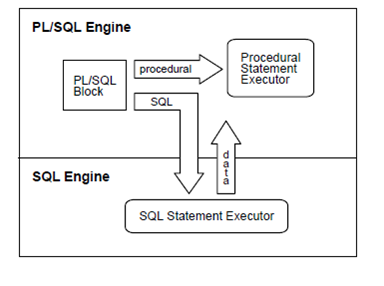
Figure: Context Switching
Each of the context switches between the PL/SQL and SQL engines adds to the overhead. Therefore, if many switches are needed, the performance suffers. That can happen when the SQL statements execute inside a loop using the collection (nested table, index-by table, varray, or the host array) elements as the bind variables. For e.g., the DELETE statement below is sent to the SQL engine with each and every iteration of the FOR loop:
DECLARE
TYPE NumList IS VARRAY(20) OF NUMBER;
depts NumList := NumList(10, 30, 70, ...); -- department numbers
BEGIN
...
FOR i IN depts.FIRST..depts.LAST LOOP
...
DELETE FROM emp WHERE deptno = depts(i);
END LOOP;
END;
In such cases, when the SQL statement affects five or more database rows, the use of bulk binds can improve the performance significantly.