Array Processing
We have seen that for executing vector operations the pipelining conception has been used. There is other method for vector operations. If we have array of n processing elements (PEs) It implies that several ALUs for storing several operands of vector then an n instruction i.e. vector addition is broadcast to all PEs , such that they sum all operands of vector at the same instance which means all PEs will perform computation in parallel. All PEs are synchronised under one control unit. This organisation of synchronous array of PEs for vector operations is termed as Array Processor. An array processor can handle one instruction and numerous data streams as we have seen in the case of SIMD organisation. So array processors are called SIMD array computers too.
The organisation of an array processor is displayed in Figure below. The subsequent elements are organised in an array processor:
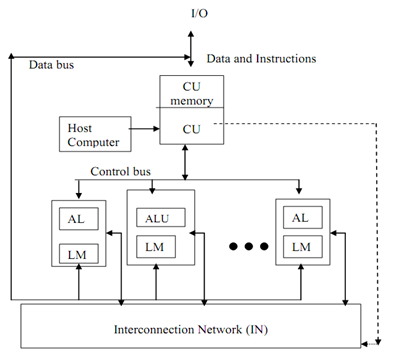
Figure: Organisation of SIMD Array Processor
Control Unit (CU): All PEs are under control of singl0065 control unit. CU manages the inter communication between the PEs. There is a local memory of control unit which is known as CY memory. The user programs are loaded in the CU memory. The vector instructions in program are decoded by CU and transmit to array of PEs. Instruction decoding and fetch is done by CU only.
Processing elements (PEs): Every processing element comprises of ALU, its registers and a local memory for storage of distributed data. This PEs has been interconnected through an interconnection network. All PEs receive instructions from the CU and several element operands are fetched from their local memory. So all PEs execute the similar function synchronously in a lock-step fashion under the control of CU.
It might be probable that all PEs require not participating in the execution of a vector instruction. So it is needed to adopt a masking technique to control the status of every PE. A masking vector is used to manage the status of all PEs such that only enabled PEs are permitted to take part in execution and others are disabled.
Interconnection Network (IN): IN executes data exchange among PEs and data routing and manipulation functions. This IN is under control of Control Unit.
Host Computer: An array processor can be connected to a host computer via the CU. The objective of the host computer is to broadcast a series of vector instructions from CU to the PEs. So host computer is a general-purpose machine which acts as a manager of entire system.
Array processors are "Special purpose computers" that have been used for the following:
- real-time scene analysis
- matrix algebra
- matrix eigen value calculations
- various scientific applications
SIMD array processor on large scale has been developed by NASA for earth resources satellite image processing. This machine has been named "Massively parallel processor" (MPP) since it comprises 16,384 processors which work concurrently. MPP provides real-time time varying scene analysis. However array processors aren't commercially popular as well as aren't commonly used. The reasons are that array processors are complicated to program in comparison to pipelining and there is a problem in vectorization.