Breadth First Search - artificial intelligence:
Given a set of operators o1, ..., on in a breadth primary search, every time a new state s is reached, an action for every operator on s is added to the bottom of the plan, for example the pairs (s,o1), ..., (s, on) are added to the end of the agenda in that order.
Thus , once the 'D' state had been found, the actions:
1. (empty, add ' N')
2. (empty, add 'A')
3. (empty, add 'D')
would be added to the top of the plan, so it would look like this:
4. ('D',add 'D')
5. ('D',add 'A')
6. ('D',add 'N')
we can remove the first agenda item as this action has been undertaken, however . There are actually five actions on the plan after the first step in the search space. Certainly, after each step, one action will be removed (the action just carried out), and 3 will be added, making a total addition of 2 actions to the plan. It turns out that this kind of breadth first search leads to the name 'DAN' after twenty steps. Also, after the 20th step, there are forty three tasks still on the plan to do.
It's helpful to think of this search as the evolution of a tree, and the diagram below shows how every string of letters is searched from the search in a breadth first manner. The numbers described above the boxes indicate at which step in the search the string was found.
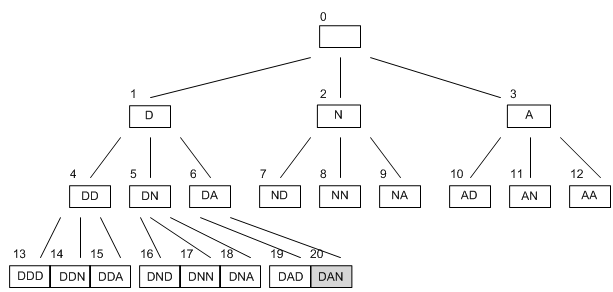
We see that every node leads to3 others, that corresponds to the fact that after each step, 3 more steps are add on the plan. This is called the branching rate of a search, and seriously affects both how long a search is going to take and how much memory it will utilized in .
Breadth initial search is a full strategy: given enough time and memory, it will find a solution if one exists. Unluckily, memory is a great problem for breadth first search. We may think about how big the plan grows, but in real we are just counting the number of states that are still 'alive', for example , there are still steps in the plan involving them. In the above diagram, the states which are still alive are those with fewer than 3 arrows coming from them: there are fourteen in all.
It's easy to show that in a search with a branching rate of b, if we want to search all the way to a depth of d, then the biggest number of states the agent will have to store at any one time is bd-1. i.e., if our professor wanted to find for all names up to length eight, she would have to remember (or write down) 2187 different strings to complete a breadth first search. This is because she would have to remember thirty seven strings of length seven in order to be able to build all the strings of length eight from them. In searches with a greater branching rate, the memory requirement may often become too big for an agent's processor.