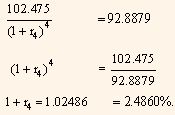In bootstrapping method, on-the-run treasury issues are used as they are fairly priced, and there is no credit risk or liquidity risk involved. In practice observed yield is rarely used for on-the-run treasury coupon issues. Instead, the coupon rate is adjusted in a way that the price of an issue would be equal to par value.
Using the treasury par yield curve, let us see the calculation of the spot rates. The treasury par yield curve and the spot rates obtained using them are shown in table 8. In this table, the par yield curve shown is for 24 treasury securities and the longest maturity is 12 years.
Table: Hypothetical Treasury Par Yield Curve
|
Period
|
Years
|
Annual Yield to Maturity (in %)
|
Price
|
Spot Rate (in %)
|
|
1
|
0.5
|
4.00
|
-
|
4.0000
|
|
2
|
1.0
|
4.20
|
-
|
4.2000
|
|
3
|
1.5
|
4.60
|
100.00
|
4.6109
|
|
4
|
2.0
|
4.95
|
100.00
|
4.9721
|
|
5
|
2.5
|
5.30
|
100.00
|
5.3382
|
|
6
|
3.0
|
5.60
|
100.00
|
5.6558
|
|
7
|
3.5
|
5.90
|
100.00
|
5.9790
|
|
8
|
4.0
|
6.10
|
100.00
|
6.1949
|
|
9
|
4.5
|
6.15
|
100.00
|
6.2449
|
|
10
|
5.0
|
6.25
|
100.00
|
6.3498
|
|
11
|
5.5
|
6.35
|
100.00
|
6.4603
|
|
12
|
6.0
|
6.45
|
100.00
|
6.5732
|
|
13
|
6.5
|
6.55
|
100.00
|
6.6887
|
|
14
|
7.0
|
6.65
|
100.00
|
6.8068
|
|
15
|
7.5
|
6.75
|
100.00
|
6.9275
|
|
16
|
8.0
|
6.80
|
100.00
|
6.9835
|
|
17
|
8.5
|
6.88
|
100.00
|
7.0828
|
|
Period
|
Years
|
Annual Yield to Maturity (in %)
|
Price
|
Spot Rate (in %)
|
|
18
|
9.0
|
6.95
|
100.00
|
7.1702
|
|
19
|
9.5
|
7.00
|
100.00
|
7.2309
|
|
20
|
10.0
|
7.09
|
100.00
|
7.3531
|
|
21
|
10.5
|
7.18
|
100.00
|
7.4785
|
|
22
|
11.0
|
7.25
|
100.00
|
7.5756
|
|
23
|
11.5
|
7.35
|
100.00
|
7.7248
|
|
24
|
12.0
|
7.50
|
100.00
|
7.9647
|
The 6-month and 1-year treasury securities are called treasury bills and they are issued as zero-coupon instruments. The annualized yield for the 6-month treasury securities and the 1-year treasury securities is equal to their respective spot rates. The value of 1.5-year Treasury rate is computed from the present value of the cash flows from the 1.5-year coupon treasury security. The spot rate at the time of receipt is used as the discounting factor. Since all coupon bonds are selling at par i.e., $100, the coupon rate would be the yield to maturity for each bond.
|
0.5 year
|
- 0.046 ´ $100 ´ 0.5
|
=
|
$2.3
|
|
1.0 year
|
- 0.046 ´ $100 ´ 0.5
|
=
|
$2.3
|
|
1.5 years
|
- 0.046 ´ $100 ´ 0.5 + 100
|
=
|
$102.3
|
The present value of the cash flows is then:
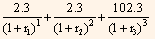
Where,
r1 = one-half the annualized 6-month theoretical spot rate.
r2 = one-half the 1-year theoretical spot rate.
r3 = one-half the 1.5-year theoretical spot rate.
We know that the 6-month spot rate is 4.00% and the 1-year spot rate is 4.02%, therefore:
r1 = 0.020 and r2= 0.021
Present value of the 1.5-year coupon Treasury security can be calculated as follows:
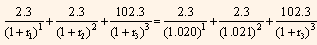
Equating the price of 1.5-year coupon Treasury security to the par value of the security, we get:
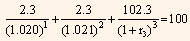
Solving the above equation we get,
2.2549 + 2.2064 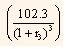 = 100
= 100
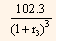 = 95.5387
= 95.5387
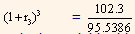
Bond-equivalent yield which is the theoretical 1.5-year spot rate is equal to 4.6109% (2 x 2.3054%). This is the rate to be used to value all the treasury cash flows that are to be received 1.5 years from now
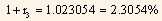
We can compute the theoretical 2-year spot rate with the help of the given theoretical 1.5-year spot rate as follows:
|
0.5 year -
|
0.0495 ´ $100 ´ 0.5
|
=
|
$2.475
|
|
1.0 year -
|
0.0495 ´ $100 ´ 0.5
|
=
|
$2.475
|
|
1.5 years -
|
0.0495 ´ $100 ´ 0.5
|
=
|
$2.475
|
|
2.0 years -
|
0.0495 ´ $100 ´ 0.5 + 100
|
=
|
$102.475
|
The present value of cash flows is:
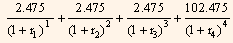
Where,
r4 = one-half the 2-year theoretical spot rate.
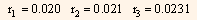
Substituting the values of r1, r2 and r3 in the above equation, we get:
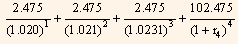
Equating the price of the 2-year coupon Treasury security to the par value of the security, we get:
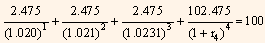
The theoretical 2-year spot rate is then: