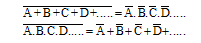Boolean algebra.
Boolean algebra mathematical method based on human reasoning. In Boolean algebra only two states exist; true and false which are written as 1 (true) and 0 (false). Boolean variables can only take one of these two values. The basic laws of Boolean algebra govern how an expression can be manipulated. The first three laws define the basic Boolean operations NOT, AND and OR.
1) Definition of NOT.
NOT(True) = False 1¯ ->0
NOT(False) = True 0‾ ->1
2) Definition of AND (two variables).
False.AND.False = False 0.0 = 0
False.AND.True = False 0.1 = 0
True.AND.False = False 1.0 = 0
True.AND.True = True 1.1 = 1
3) Definition of OR (two variables).
False.OR.False = False 0 + 0 = 0
False.OR.True = True 0 + 1 = 1
True.OR.False = True 1 + 0 = 1
True.OR.True = True 1 + 1 = 1
4) Zero and unit rules (here we introduce the Boolean variable, X, which can be either true or false).
True.AND.X = X 1.X = X
False.AND.X = False 0.X = 0
True.OR.X = True 1 + X = 1
False.OR.X = X 0 + X = X
5) Complement relations.
X.AND.(NOT(X)) = False
X.OR.(NOT(X)) = True
NOT(NOT(X)) = X
6) Idempotence.
X + X = X
X.X = X
7) Commutative laws (now have two variables X and Y).
X + Y = Y + X
X.Y = Y.X
8) Associative laws (insertion of brackets).
X + Y + Z = X + (Y + Z) = (X + Y) + Z
X.Y.Z = X.(Y.Z) = (X.Y).Z
9) Distribution laws.
X.(Y + Z) = X.Y + X.Z
X + Y.Z = (X + Y).(X + Z)
10) Absorption rules.
X + X.Y = X
X.(X + Y) = X
11) de Morgan's Theorem (for any number of variables).