Benchmarking is a efficient tool that permits a company to decide whether its performance of organizational procedures and activities correspond to the best practices. Benchmarking models are helpful in determining how well a business division, unit, organization or corporation is performing compared with other like organizations. A benchmark is referred to as a point of reference for a measurement. The term 'benchmark' most probably originates from the practice of creating dimensional height measurements of an object on a workbench by means of a gradual scale or related tool, and using the surface of the workbench as the source for the measurements.
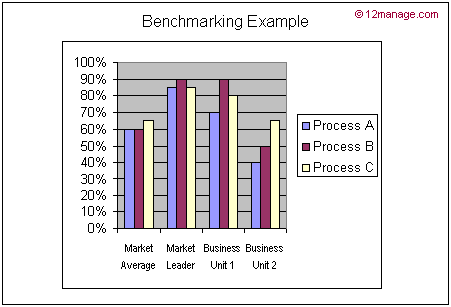
Business benchmarking is associated with Kaizen and competitive advantage thinking.
Use of Benchmarking
• Budgetary reasons
• Improving communication
• Professionalizing the organization / processes, or for
• In outsourcing projects
Five types of Benchmarking
There are five types of benchmarking
1. Internal benchmarking (benchmark created within a corporation, for example among business units)
2. Functional benchmarking (benchmark for similar processes in an industry)
3. Collaborative benchmarking
4. Competitive benchmarking (benchmark for performance or procedures with competitors)
5. Generic benchmarking (For comparison of operations between not related industries)
Typical steps in a benchmarking process
• Scope or definition of a process
• Select benchmark partner(s)
• Find out measurement methods, units, indicators and data collection method
• Data compilation
• Study of the discrepancies
• Present the consequences and discuss implications / improvement areas and objectives
• Make enhancement plans or new measures
• Check progress and plan ongoing benchmark.
Limitations of benchmarking
• It is a tough process that requires a lot of commitment to be successful.
• Expensive and Time-consuming.