Q. Basic Characteristics and Operation of MOSFET ?
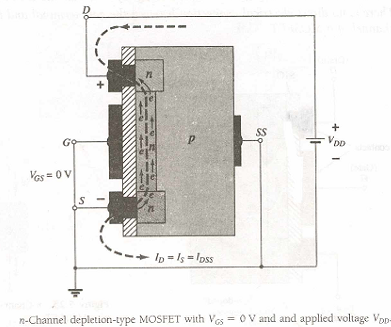
In Figure the gate-to-source voltage is set to zero volts by the direct connection from one terminal to the other, and a voltage V DS is applied across the drain-to-source terminals. The result is an attraction for the positive potential at the drain by the free electrons of the n- channel and a current similar to that established through the channel of the JFET. In fact, the resulting current with VDS = 0 V continues to be labeled IDss, as shown in Figure.
In Figure, VDS has been set at a negative voltage such as -1 V. The negative potential at the gate will tend to pressure electrons toward the p-type substrate (like charges repel) and attract holes from the p-type substrate (opposite charges attract) as shown in Figure.
Depending on the magnitude of the negative bias established by VDS, a level of recombination between electrons and holes will occur that will reduce the number of free electrons in the n-channel available for conduction. The more negative the bias, the higher the rate of recombination. The resulting level of drain current is therefore reduced with increasing negative bias for VDS as shown in Figure for VDS = -1V,-2V, and so on, to the pinch-off level of - 6 V. The resulting levels of drain current mid the plotting of the transfer curve proceeds exactly as described for the JFET.
For positive values of V GS' the positive gate will draw additional electrons (free carriers) from the p-type substrate due to the reverse leakage current and establish new carriers through the collisions resulting between accelerating particles. As the gate-to-source voltage continues to increase in the positive direction, the drain current will increase at a rapid rate for the reasons listed above. The vertical spacing between the V GS = 0 V and V GS = + 1 V curves of Fig is a clear the application of a voltage V GS = + 4 V would result in a drain current of 22.2 mA, which could possibly exceed the maximum rating (current or power) for the device. As revealed above, the application of a positive gate-to-source voltage has "enhanced" the level of free carriers in the channel compared to that encountered with V GS = 0 V.