Assignment Statement:
The assignment statement sets the present value of the variable, parameter, field, or element. The statement consists of an assignment target followed by an assignment operator and an expression. Whenever the statement is executed, the expressions evaluate and the resulting value is stored in the target.
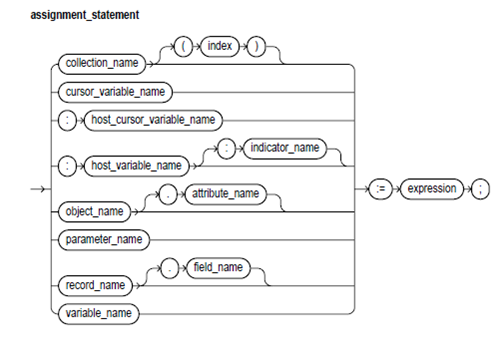
Keyword and Parameter Description
1) collection_name:
These identify an index-by table, nested table, or varray previously declared within the present scope.
2) cursor_variable_name:
These identify a PL/SQL cursor variable formerly declared within the present scope. Only the value of the other cursor variable can be assigned to a cursor variable.
3) host_cursor_variable_name:
These identify a cursor variable declared in the PL/SQL host atmosphere and passed to the PL/SQL as a bind variable. The host cursor's datatype variable is well-suited with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable. The host variables have to be prefixed with a colon.
4) host_variable_name:
These identify a variable declared in the PL/SQL host atmosphere and passed to the PL/SQL as a bind variable. The host variables should be prefixed with a colon.
5) object_name:
These identify an object (instance of the object type) formerly declared within the present scope.
6) indicator_name:
These identify an indicator variable declared in a PL/SQL host atmosphere and passed to the PL/SQL. The Indicator variables should be prefixed with a colon. The indicator variable "indicates" the value or condition of its related host variable. For illustration, in the Oracle Precompiler atmosphere, the indicator variables let you detect nulls or truncated values in the output host variables.
7) parameter_name:
These identify the formal OUT or IN OUT parameter of the subprogram in which the assignment statement become visible.
8) index:
This is a numeric expression that should results a value of the type BINARY_INTEGER or a value implicitly convertible to that datatype.
9) record_name.field_nameP:
These identify the field in a user-defined or %ROWTYPE record earlier declared within the present scope.
10) variable_name:
These identify a PL/SQL variable earlier declared within the present scope.