Assessing Heuristic Searches
Given a specific problem you want to create an agent to solve, there can be more than one way of specifying it as a search problem, more than one option for the search strategy and different possibilities for heuristic measures. To a large extent, it is hard to predict what the best option will be, and it will require some experimentation to find out them. In some kind of cases, - if we calculate the effective branching rate, as described below - we may tell for sure if one heuristic measure is always being out-performed by another.
The Effective Branching Rate
Assessing heuristic functions is an essential part of Artificial Intelligence research: a specific heuristic function can sound like a good idea, but in practice give no discernible increase in the quality of the search. Search quality may be determined experimentally in terms of the output from the search, and by using sevral measures likewise the effective branching rate. Imagine a specific problem P has been solved by search strategy S by expanding N nodes, and the solution lay at depth D in the space. Then the effective branching value of S for P is calculated by comparing S to a uniform search U. An example of a uniform search is a breadth first search where many branches from any node are always the same (as in our baby naming example). We then suppose the (uniform) branching rate of U is like that, on exhausting its search to depth D, it too would have expanded defiantly N nodes. This imagined branching rate, written b*, is the effective branching rate of S and is calculated thus:
N = 1 + b* + (b*)2 + ... + (b*)D.
Rearranging this equation will give a value for b*. For an example (taken from Norvig and Russell )imagine S finds a solution at depth 5 having expanded 52 nodes. In this type of case:
52 = 1 + b* + (b*)2 + ... + (b*)5.
and it turns out that b*=1.91. To calculate its value , we use the well known mathematical identity:
This make us enables to write a polynomial for which b* is a 0, and we may solve this using numerical techniques such as Newton's method.
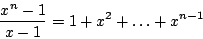
It is typically the case that the effective branching rate of a search strategy is same over all the problems it is used for, because of this it is suitable to average b* over a small set of problems to give a valid account. If a heuristic search has a branching rate near to 1, then it is a good sign. We say that 1 heuristic function h1 dominates another h2 if the search using h1 always has a lower effective branching rate than h2. Having a lower effective branching rate is obviously desirable because it means a quicker search.