Arc Length - Applications of integrals
In this part we are going to look at determining the arc length of a function. As it's sufficiently easy to derive the formulas that we'll utilize in this section we will derive one of them and leave the other to you to derive.
We want to find out the length of the continuous function
y = f (x) on the interval [a, b].
Primarily we'll need to find out the length of the curve. We'll do this by dividing the interval up into n equal subintervals each of width Δx and we'll indicate the point on the curve at each point by Pi. We can then estimate the curve by a series of straight lines connecting the points. Now Here is a sketch of this situation for n = 9.
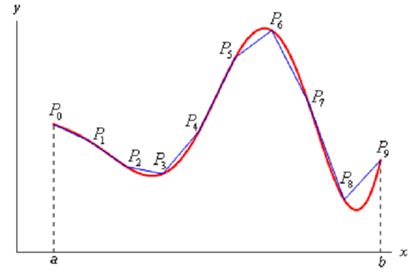
Now indicate the length of every line segments by then be approximately, |Pi -1 Pi| and the length of the curve will
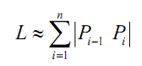
and after that we can obtain the exact length by taking n larger and larger. Alternatively, the exact length will be,
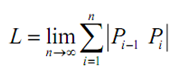
Now here, let's get a good grasp on the length of each of these line segments. Very first, on each segment let's illustrate Δyi = yi - yi-1 = f (xi) - f (xi-1) . After that we can calculate directly the length of the line segments like this:
|Pi-1 Pi| = √ ((xi - xi-1)2 + (yi - yi-1)2)
= √(Δx2 +Δy2i).
By using the Mean Value Theorem we make out that on the interval [xi-1, xi] there is a point x*i that is why,
F (xi) - f (xi-1)
= f' (x*i) (xi - xi-1)
Δyi= f' (x*i)Δx
Hence, the length can now be written as,
|Pi-1 Pi| = √ ((xi - xi-1)2 + (yi - yi-1)2)
= √(Δx2 +[f' (xi*)]2 Δx2 )
= √ (1 + [f' (xi*)]2 Δx)
The exact length of the curve is then,
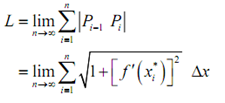
Though, by using the definition of the definite integral, this is nothing much more than,
L - ∫ba√ (1+[f' (x)]2 dx)
A little more suitable notation (according to me) is the following.
L = ∫ba √ (1 + (dy/dx)2 dx)
In a identical way we can also derive a formula for x = h(y) on [c,d]. This formula is,
L - ∫bc√ (1+[h' (y)]2 dy)
∫bc √ (1 + (dx/dy)2 dy)
Once Again, the second form is possibly a much more convenient.
Note: the variation in the derivative under the square root! Don't get so confused. With one we distinguish with respect to x and with the other we distinguish with respect to y. One way to maintain the two straight is to note that the differential in the "denominator" of the derivative will match up along with the differential in the integral. This is one of the causes why the second form is a little much more suitable.
Previous to we work any instance we need to make a small change in notation. In place of having two formulas for the arc length of a function we are going to decrease it, in part, to a single formula. From this point on we are going to make use of the following formula for the length of the curve.