In computer programming, Trees are utilized enormously. These can be utilized for developing database search times (binary search trees, AVL trees, 2-3 trees, red-black trees), Game programming (decision trees, minimax trees, pathfinding trees),
3D graphics programming (octrees, quadtrees,), Arithmetic Scripting languages (arithmetic precedence trees), Data compression (Huffman trees), and file systems (sparse indexed trees, B- trees, tries ). Figure illustrated a tic-tac-toe game tree illustrating various stages of game.
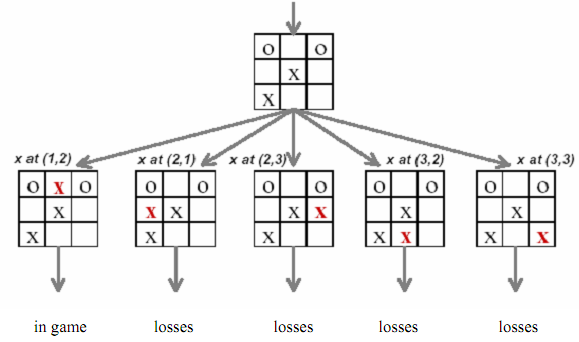
Figure: A tic-tac-toe game tree showing various stages of game
In the entire above scenario except the first one, ultimately the player (playing with X) looses in subsequent moves.
The General tree (also known as Linked Trees) is a generic tree which has one root node, and each node in the tree can have limitless number of child nodes. One popular employ of this kind of tree is in Family Tree programs. In game programming, several games use these types of trees for decision-making processes as illustrated above for tic-tac-toe. A computer program might have to make a decision depend on an event that happened.
But it is just a simple tree for demonstration. A more complicated AI decision tree would absolutely have a lot more options. The interesting thing regarding using a tree for decision-making is that the options are cut down for each level of the tree as we go down, very much simplifying the subsequent moves & raising the speed at which the AI program makes a decision.
The big problem along with tree based level progressions, but, is that sometimes the tree can get too large & complex as the number of moves (level in a tree) enhance. Suppose a game offering just two choices for every move to the next level at the end of every level in a ten level game. This would need a tree of 1023 nodes to be created.
Binary trees are utilized for searching keys. Such trees are called Binary Search trees
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a binary tree having the given properties:
1. Always the key of a node is greater than the keys of the nodes in its left sub-tree
2. Always the key of a node is smaller than the keys of the nodes in its right sub-tree
It might be seen that while nodes of a BST are traversed by inorder traversal, the keys appear in sorted order:
inorder(root)
{ inorder(root.left) print(root.key) inorder(root.right)
}
Binary Trees are also utilized for evaluating expressions.
A binary tree can be utilized to represent & evaluate arithmetic expressions.
1. If a node is a leaf, then the element in it indicates the value.
2. If this is not leaf, then appraise the children & join them in according to the operation indicated by the element.