Low grade oxide, sulphide and carbonate ores of copper are treated with dilute sulphuric acid in the existence of oxygen:
CuO+ H2SO4------------------> CuSO4+ H2O
CuCO3+ H2SO4--------------> CuSO4+ CO2+ H2O
Cu2S+ 2H2SO4+ 2O2--------> 2CuSO4+ SO2+ 2H2O
When the silver ore, AgCI, is reacted with an aqueous solution of sodium cyanide, AgCl dissolves in it due to the formation of Na[Ag(CN)2]:
AgCl+ 2NaCN--------------> Na[Ag(CN2) 2]+ NaCl
Sulphide ore, Ag2S, dissolves only gradually, as the reaction is reversible:
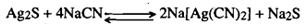
If air is passed through this solution, sodium sulphide is oxidised to sodium sulphate and the forward reaction goes to completion dissolving all the sulphide ore. In the existence of air, native silver is also leached out in the form of Na [Ag(CN)2]:
4Ag+ 8NaCH + 2H2O + O2------------> 4Na [Ag (CN) 2] + 4NaOH
The leached out metals are taken from the solution either by precipitation on treatment with a more electropositive metal or by electrolysis. For Illustration, copper will be recovered from its solution by adding metals like Al, Fe etc. Silver is obtained from its solution by treatment with Al or Zn:
CuSO4 + Fe----------> Cu + FeSO4
2Na [Ag(CN)2]+ Zn ---------> 2Ag+ Na2 [ Zn(CN)4]
Alternatively, the dilute solution will be concentrated and then electrolysed to get pure metals. From leached solution of copper ores, copper is usually recovered by electrolysis of the solution. In electrolysis the anode used is of lead alloy and the cathode is of a pure copper sheet. When direct current is goes through the solution, copper gets deposited on cathode. Sulphuric acid is prepared during electrolysis which is recycled in leaching of ore. Given reactions take place during electrolysis:
Anode: 2H2O ------------> O2 (g) + 4H+ (aq) + 4e
Cathode: Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e---------> Cu (s)
2H+ (aq) + SO2-4(aq) --------> H2So4 (aq)