Anti Aliasing - Modeling and Rendering
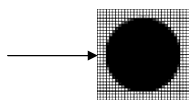
It is a method for enhancing the realism of an image through eliminating the jagged edges from it. Such jagged edges or "jaggies", appear since a computer monitor has square pixels, and these square pixels are inadequate for displaying lines or curves which are not parallel to the pixels and the other reason is low sampling rate of the image information, that in turn cause such jaggies quite same to star casing discussed in previous under DDA algorithm. For better understanding, get the subsequent image of darkened circle as:
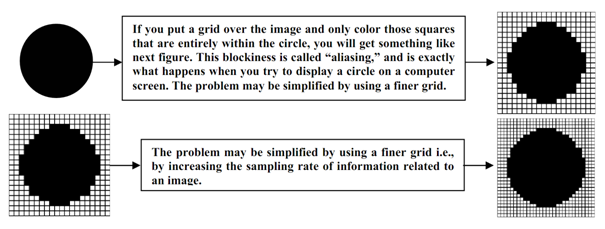
It is impossible to completely remove aliasing since computers are digital discrete in nature. Though, it is not impossible to minimize aliasing, the solutions utilized by ray tracers today engage treating all pixels as a finite square area that, in fact as they are, quite than as a mere point on the screen. Conversely, the pixel must not be taken as a point or area although should be taken as a sample of image information as higher the sampling is lesser the aliasing is. Here let us discuss how suitably the sampling can be complete: Rays are fired in the scene by the centers of the pixels and the intensities of adjacent rays are evaluated. If they be different by several pre-determined amount, more rays are fired in the surfaces of the pixels. The intensities of each ray shot in a specified pixel are then averaged to determine a color which better fits what would be expected at such point.
Note: Do not treat a pixel like a square area, when this does not generate correct filtering behavior, actually a pixel is not a point, although it is a sample of information to be displayed.
Anti-aliasing, it assists eliminate jagged edges and to create an image seem more realistic. Continuing the above illustration, the anti-aliased circle might, after that be represented