Although how will the system recover
The selection of REDO or UNDO for a transaction for the recovery is completed on the basis of the state of the transactions. This state is given in two steps:
- Look into the log file and search all the transactions that have started. For instance, in Figure, transactions T1, T2 and T3 are applicants for recovery.
- Search those transactions that have committed. REDO these transactions. All different transactions have not committed so they should be rolled back, so UNDO them. For instance, in Figure UNDO will be performed on T1 and T2; and REDO will be performed on T3.
Please note that in Figure some of the values may not have yet been communicated to database, yet we require to perform UNDO as we are not sure what values have been written back to the database.
Although how will the system recover? Once the recovery operation has been particular, the systems just takes the needed REDO or UNDO values from the transaction log and alters the inconsistent state of database to a consistent state.
Let us consider various transactions with their respective start & end (commit) times as shown in Figure.
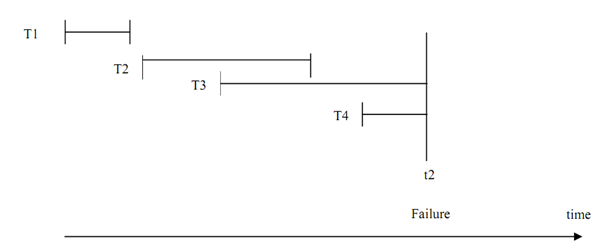
Figure: Execution of Concurrent Transactions
In the figure above four transactions are implementing simultaneously, on encountering a failure at time t2, and the transactions T1 and T2 are to be REDONE and T3 and T4 will be UNDONE. But take a system that has thousands of parallel transactions then every transaction that have been committed may have to be redone and every uncommitted transaction requires being undone. That is not a very good choice as it needs redoing of even those transactions that might have been committed even hours previous. So can we progress on this situation? Yes, we can take checkpoints. Figure shows a checkpoint mechanism:
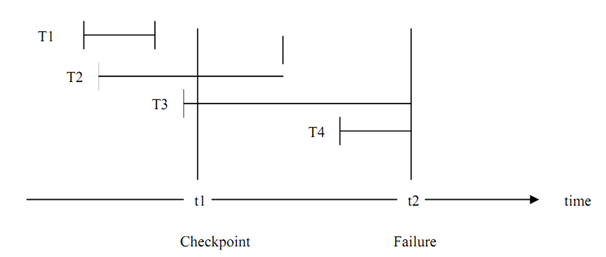
Figure: Checkpoint In Transaction Execution
A checkpoint is taken at time t1 and a failure occurs at time t2. Checkpoint transfers every committed change to database and all the system logs to stable storage (it is described as the storage that would not be lost). At restart time after the failure the stable check pointed state is restored. Therefore, we require to only REDO or UNDO those transactions that have done or started after the checkpoint has been taken. The only possible drawbacks of this scheme may be that during
the time of taking the checkpoint the database would not be available and some of the uncommitted values might be put in the physical database. To overcome the primary problem the checkpoints should be taken at times when system load is low. To avoid the second problem some systems permit some time to the ongoing transactions to complete without restarting new transactions.
In the case of Figure the recovery from failure at t2 will be as follows:
- The transaction T1 will not be considered for recovery as the changes made by it have already been committed and transferred to physical database at checkpoint t1.
- The transaction T2 since it has not committed till the checkpoint t1 except have committed before t2, will be REDONE.
- T3 must be UNDONE as the changes made by it before checkpoint (we do not know for sure if any such changes were made prior to checkpoint) must have been communicated to the physical database. T3 must be restarted with a new name.
- T4 begin after the checkpoint, and if we strictly follow the scheme in which the buffers are written back only on the checkpoint, then nothing required to be done except restarting the transaction T4 with a new name.
The restart of a transaction needs the log to keep information of the new name of the transaction and maybe give higher priority to this newer transaction.
But one question is still unanswered that is during a failure we lose database information in RAM buffers, we might also lose log as it may also be stored in RAM buffers, so how does log make sure recovery?
The answer to this question lies in the fact that for storing transaction log we follow a Write Ahead Log Protocol. As according to this protocol, the transaction logs are written to stable storage before any item is updated. Or more particularly it can be stated as; the undo potion of log is written to stable storage prior to some updates and redo portion of log is written to stable storage prior to commit.
Log based recovery scheme can be used for any kind of failure given you have stored the most recent checkpoint state and most recent log as per write ahead log protocol into the stable storage. Stable storage from the point of view of external failure needs more than one copy of such data at more than one location.