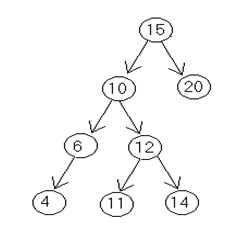
Q. Write down an algorithm to delete the specific node from binary search tree. Trace the algorithm to delete a node (10) from the following given tree.
Ans.
Algorithm for Delete ting the specific Node From the Binary Search Tree
To delete the specific node following possibilities may arise
1) Node id a terminal node
2) Node have only one child
3) Node having 2 children.
DEL(INFO, LEFT, RIGT, ROOT, AVAIL, ITEM)
A binary search tree T is in the memory, and an ITEM of information is given as follows.
This algorithm deletes the specific ITEM from the tree.
1. [to Find the locations of ITEM and its parent] Call FIND(INFO, RIGHT, ROOT, ITEM, LOC, PAR).
2. [ITEM in tree?]
if LOC=NULL, then write : ITEM not in tree, and Exit.
3. [Delete node containing ITEM.]
if RIGHT[LOC] != NULL and LEFT[LOC] !=NULL then:
Call CASEB(INFO,LEFT,RIGHT,ROOT,LOC,PAR). Else:
Call CASEA (INFO,LEFT,RIGHT,ROOT,LOC,PAR).
[End of if structure.]
4. [Return deleted node to AVAIL list.] Set LEFT[LOC]:=AVAIL and AVAIL:=LOC.
5. Exit.
CASEB(INFO,LEFT,RIGHT,ROOT,LOC,PAR)
This procedure will delete the node N at LOC location, where N has two children. The pointer PAR gives us the location of the parent of N, or else PAR=NULL indicates that N is a root node. The pointer SUC gives us the location of the inorder successor of N, and PARSUC gives us the location of the parent of the inorder successor.
1. [Find SUC and PARSUC.]
(a) Set PTR: = RIGHT[LOC] and SAVE:=LOC. (b) Repeat while LEFT[PTR] ≠ NULL:
Set SAVE:=PTR and PTR:=LEFT[PTR]. [End of loop.]
(c) Set SUC : = PTR and PARSUC:=SAVE.
2. [Delete inorder successor]
Call CASEA (INFO, LEFT, RIGHT, ROOT, SUC, PARSUC).
3. [Replace node N by its inorder successor.] (a) If PAR≠NULL, then:
If LOC = LEFT[PAR], then: Set LEFT[PAR]:=SUC.
Else:
Set RIGHT[PAR]: = SUC. [End of If structure.]
Else:
Set ROOT: = SUC. [End of If structure.]
(b) Set LEFT[SUC]:= LEFT [LOC] and
RIGHT[SUC]:=RIGHT[LOC]
4. Return.
CASEA(INFO, LEFT, RIGHT, ROOT, LOC, PAR)
This procedure deletes the node N at LOC location, where N does not contain two children. The pointer PAR gives us the location of the parent of N, or else PAR=NULL indicates that N is a root node. The pointer CHILD gives us the location of the only child of the N, or else CHILD = NULL indicates N has no children.
1. [Initializes CHILD.]
If LEFT[LOC] = NULL and RIGHT[LOC] = NULL, then: Set CHILD:=NULL.
Else if LEFT[LOC]≠NULL, then:
Set CHILD: = LEFT[LOC].
Else
Set CHILD:=RIGHT[LOC] [End of If structue.]
2. If PAR ≠ NULL, then:
If LOC = LEFT [PAR], then:
Set LEFT[PAR]:=CHILD.
Else:
Set RIGHT[PAR]:CHILD = CHILD [End of If structure.]
Else:
Set ROOT : = CHILD.
[End of If structure.]
3. Return.
Inorder traversal of the tree is
4 6 10 11 12 14 15 20
To delete 10
PAR = Parent of 10 ie 15
SUC = inorder succ of 10 ie. 11
PARSUC = Parent of inorder succ ie 12
PTR = RIGHT [LOC]
Address of 12 SAVE: = address of 10
SAVE: = address of 12
PTR = address of 11
SUC = ADDRESS OF 11
PAR SUCC:= ADDRESS OF 12
CHILD = NULL
LEFT [PARSUC] = CHILD= NULL LEFT [PAR]= ADDRESS OF 11
LEFT [SUC] = LEFT [LOC] = ADDRESS OF 6
RIGHT [SUC] = RIGHT[LOC] = ADDRESS OF 12