Long Run Equilibrium:Graphical Analysis
In the long run the natural rate of output is the level of output to which the economy will tend to adjust in the long run. This indicates that in the long run the average price level has no effect on the level of output (Y). As discussed earlier, any unanticipated price rise in the short run will be offset in the long run by an increase in costs as contracts with the suppliers of inputs are renegotiated. Therefore, in the long run the output of an economy does not depend on the price level, but on factors such as, labor import costs, capital stock, technological progress, etc. These factors are not influenced by changes in the average price level and so is the case with aggregate supply in the long run. Therefore, as shown in figure 6.5, in the long run the aggregate supply curve of an economy is vertical at the natural rate of output.
Figure shows the relationship among aggregate demand curve (AD), the short run aggregate supply curve (ASS) and the long run aggregate supply curve (ASL). The output demanded and supplied per period of time, say per year, are designated by Q. Recall that the natural rate of output (Q) is not the same as the level of output achieved in the short run when all resources are fully employed. At this level of output there are unemployed resources caused by lack of mobility and other labor market rigidities which cannot be reduced by raising aggregate demand.
Figure: Aggregate Supply in the short run and in the long run
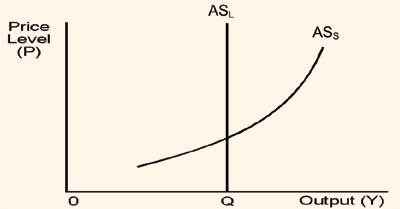
Figure: Short Run and Long Run Equilibrium between Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
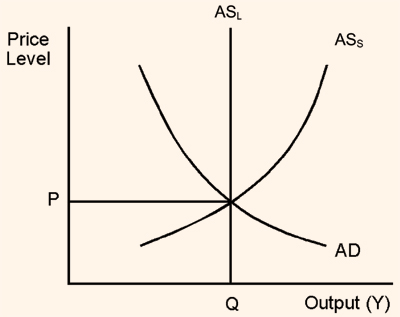
It is shown that as long as aggregate demand and aggregate supply conditions for the natural rate of output continue to be those represented by the AD, ASS and ASL curves the market for this output can be in equilibrium condition provided the output actually supplied and demanded is at Q and the price is P. Only this combination of price level (P) and quantity demanded (Q) will clear the market, leaving no excess supply or no excess demand.
From this analysis, there are at least two important points that will be useful for our later analysis. They are (i) market equilibrium is not determined by aggregate demand conditions alone, not by supply conditions alone, but by a combination of both (ii) both the price level and the natural rate of output and sales are determined simultaneously.