ACCOUNTING SYSTEM-EXAMPLE III
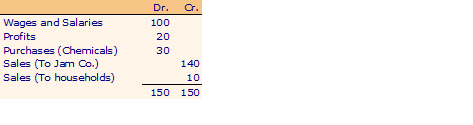
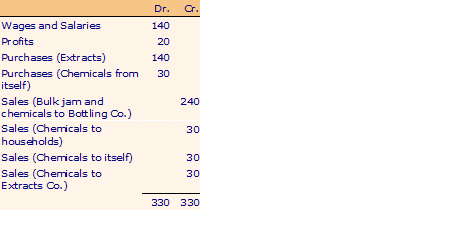
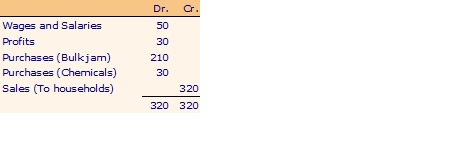
Now suppose the Jam Co. manufactures some herbal chemicals and flavors which it sells partly to Extracts Co., partly to Bottling Co., some are consumed in its own production process and some are sold directly to households. Also, some households buy fruit extracts directly from the extracts company. The accounts are as follows:
Extracts Co.
Jam Co.
Bottling and Distribution Co.
The consolidated production account can be drawn up in which all transactions within and among the firms are netted out:
Production Account
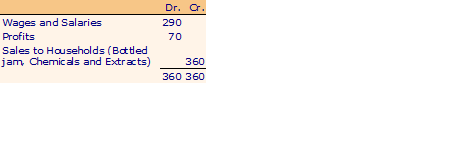
Household Account

GNP: Market value of all final sales = 320 + 30 + 10
= 360
GNI: All factor incomes earned = 290 + 70 = 360
We can set up an input-output account for this miniature economy showing transactions within the productive sector and between the productive sector and the household sector.
Transactions Table
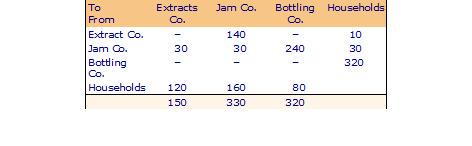
The inner table of first three rows and first three columns show the transactions within the productive sector, viz. sales and purchases of intermediate inputs. These are netted out from the national income accounts. The last row shows the value of labor and ownership services provided by the households to the three firms; or in other words 'value added' in the production sector; these constitute the factor incomes (GNI). The last column shows the purchases of households financed from these incomes (GNP).
Suppose a part of the output of bottled jam is sold by the Bottling Co. to the Extracts Co. which distributes it free to its workers at lunch time. How will this be accommodated in national accounts?