8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface
Intel's 8255 A programmable peripheral interface provides a nice instance of a parallel interface. As shown the interface have a control register and 3 separately addressable ports, denoted from A, B, and C. Whether or not an 8255A is being accessed is determined by the signal on the CS pin and the direction of the access is according to the WR and RD signals. Which of the 4 registers is being addressed is determined by the signals applied to the pins A0 and A1. So, the lowest port address assigned to an 8255 A might be divisible by 4. A review of the 8255 A's addressing is:
A1 A0 RD WR CS Transfer Description
0 0 0 1 0 Port A to data bus
0 1 0 1 0 Port B to data bus
1 0 0 1 0 Port C to data bus
0 0 1 0 0 Data bus to port A
0 1 1 0 0 Data bus to port B
1 0 1 0 0 Data bus to port C
1 1 1 0 0 Data bus to control register if D7= 1; if D7=0 input from the data bus is treated as a Set/Reset instruction
x x x x 1 D7-D0 go to high-impedance state
1 1 0 1 0 Illegal combination
x x 1 1 0 D7-D0 go to high-impedance state
Where 0 is low and 1 is high
Because the bits in port C are sometimes utilized as control bits, the 8255 A is designed so that they may be output to separately by using a Reset/set instruction. When the 8255 A receives a byte that is directed to its control register, it checked data bit 7.If this bit is one, the data are transferred to the control register, but if it is zero, the data retreated as a Reset/set instruction and is utilized to clear or set the port C it denoted by the instruction. Bits 3-1 gives the bit number of the bit to be changed and bit 0 denote whether it is to be cleared or set. The remaining bits are not useful.
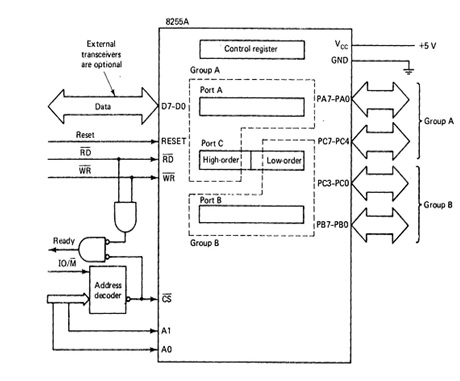
The bits in the 3 ports are attached to pins that can be linked to the I/O device. These bits are divided into groups A & B, with group A consisting of the bits in port A and the 4 MSBs of port C and group b consisting of port B and the 4 LSBs of port C. the use of each of the 2 groups is controlled by the mode connected with it. Group A is connected with 1 of 3 modes, mode zero, mode one, and mode two, and group B with 1 of 2 modes, mode 0 and mode 1.