The aim of this assignment is to develop and test your ability to integrate your knowledge of plastic failure and fracture. Below is a plot that shows the plane strain fracture toughness and yield strength for a number of aluminium alloys. Note the log scale! This will be the basis of the present assignment. Each alloy is represented by an ellipse because there is always some variation in the properties of alloys from one batch to another. You can see that in wrought alloys, the strength can be increased without a great deal of change in the fracture toughness. However, in the casting alloys, the higher strength grades show reduced fracture toughness.
1. Consider alloys 2024 T6 and A201. We want to know if either of these is likely to be adversely affected - in terms of fracture - by an accidental brush with a spinning thin angle grinder blade. Estimate the critical crack sizes for each alloy for plane strain fracture under a load of 250 MPa. Use the properties corresponding to the centre of the ellipse. Is a brush with an angle grinder likely to pose a risk for this situation? What is one reason why the fracture toughness of the casting alloys is less than the wrought alloys? (You will have to hunt around a little to find the answer to this, but it won't hurt you.)
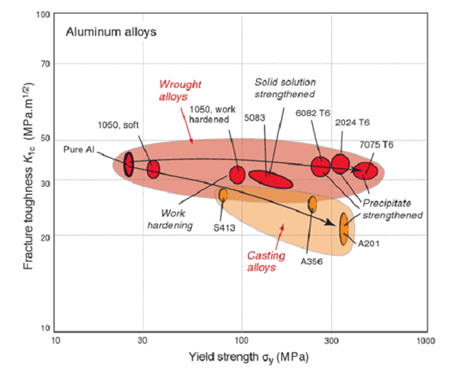
2. Consider alloy 1050 in the work hardened and soft conditions. Describe the main difference in the micro-structure between these two materials. What does work hardening affect more, yield strength or fracture strength? Imagine these alloys are loaded to a stress approximately 80% that of their yield stresses. Calculate the respective critical flaw sizes for fracture. Do you think either of these are likely to arise by accidental damage? Now imagine alloy 7075 T6 is work hardened by an equivalent amount to that seen in alloy 1050 (i.e. by about 60 MPa), without any change to its fracture toughness. This is then loaded to 80% of its yield stress. What is the critical flaw size for this material?
3. Consider the strain needed to harden 1050 by the amount seen above. Assume that hardening starts from a yield stress of soft 1050 (call this is σ0). Work hardening can then be described by adding a power law (kεn , where ε is strain, k is 100 MPa and n is 0.5) to this initial yield stress. Calculate how much strain would be required to work harden the material to the value reported above for hardened 1050.
4. It is useful to consider whether an alloy will fail by yielding or by fracture, when subjected to an overload. For instance, the pin on my trailer is designed to fail by yielding rather than fracture. Consider materials with a (conservative) flaw size of 10 mm. List the materials shown in the figure above that are likely to fail by yielding but not fracture when subjected to an overload. (That is, work out which will happen at the lower stress, yielding or fracture, for a flaw size of 10 mm.)